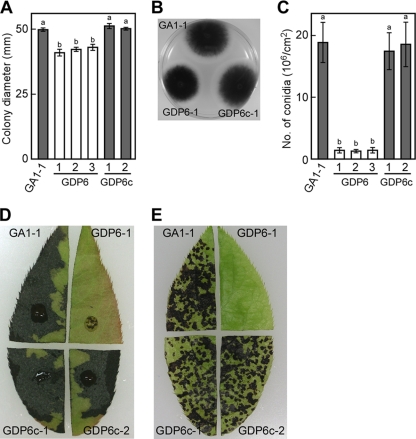
Fig. 7.
Phenotypic analysis of a ΔAaPEX6 mutant strain. (A to C) Colony growth, colony morphology, and conidiation of a ΔAaPEX6 mutant strain. Strains were grown on PDA for 5 days, and colony diameter was measured (A and B). Strains were grown on oatmeal agar for 10 days, and conidiation was induced (C). Data represent the means and standard deviations of four replications. Columns with the same letters are not significantly different; columns with different letters are different at a significance level of P ≤ 0.01 according to the Tukey-Kramer multiple-comparison test. GA1-1, GFP-Akt1-expressing strain; GDP6-1 to GDP6-3, ΔAaPEX6 mutant strains made from GA1-1; GDP6c-1 and GDP6c-2, AaPEX6-complemented strains made from GDP6-1. (D and E) AK-toxin production and pathogenicity of ΔAaPEX6 mutant strain. Leaves of Japanese pear cultivar Nijisseiki were wounded slightly, treated with culture filtrate of each strain, and incubated for 24 h (D). Leaves were spray inoculated with a conidial suspension (about 5 × 105 conidia/ml) of each strain and incubated for 24 h (E).