Figure 3.
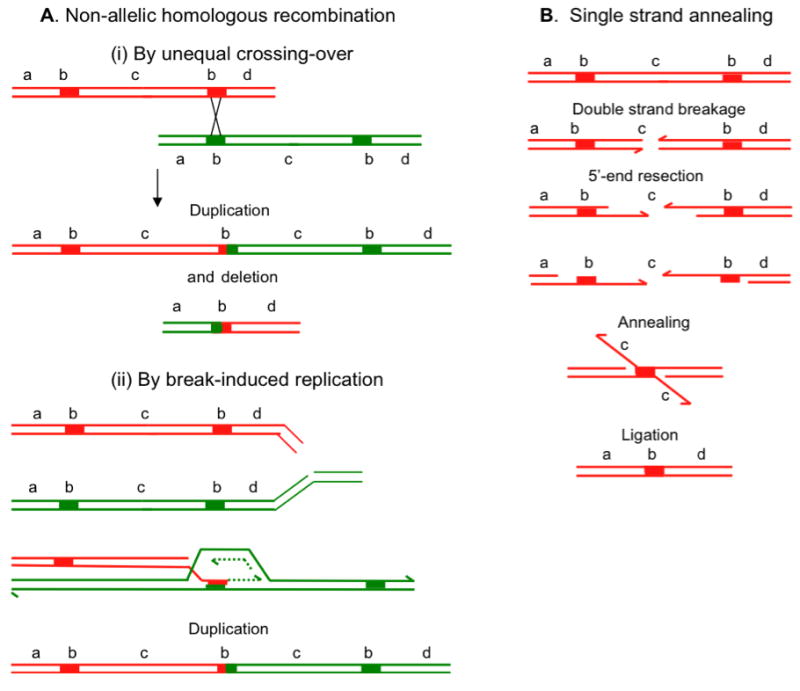
Change in copy number by homologous recombination. A. Non-allelic homologous recombination (NAHR). (Aa) If a recombination repair event uses a direct repeat (b) as homology, a crossover outcome (shown as an “x”) leads to products that are reciprocally duplicated and deleted for sequence (c) between the repeats. These might segregate from each other at the next cell division, thus changing the copy number in both daughter cells. NAHR can also occur by BIR when the broken molecule uses ectopic homology to restart the replication fork (Ab). BIR will form duplications and deletions in separate events. B. Single-strand annealing. When 5′ end resection on either side of a double-strand break does not lead to invasion of homologous sequence, resection continues. If this resection reveals complementary single-stranded sequence (b) shown by thickened lines, these can anneal. Removal of flaps, gap-filling and ligation complete repair of the double-strand break with deletion of the sequence between the repeats (c) and of one of the repeats. Each line represents a single DNA strand, polarity is indicated by half arrows on 3′ ends, and specific sequences are identified by letters “a” to “d”.
