Figure 2.
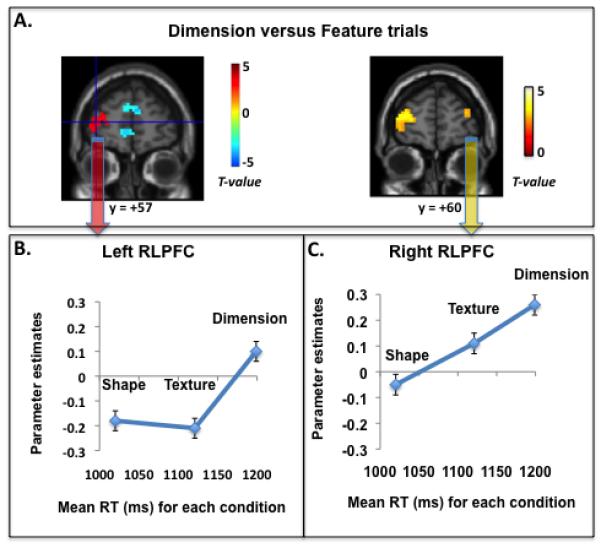
fMRI results for our relational matching task (N=15). A. A whole-brain comparison of Dimension versus Feature tasks (p < .005 uncorrected, >10 voxels) revealed that left RLPFC was relatively more engaged by Dimension trials, whereas rostromedial PFC was relatively more engaged by Feature trials. At a liberal statistical threshold (p < .01 uncorrected), right RLPFC was also engaged by Dimension relative to Feature trials. Shown in B. and C. are plots of RLPFC parameter estimates for each condition relative to the resting baseline. The x-axis features the mean RT for each condition; Shape RTs were faster than Texture RTs, which in turn were numerically but not statistically faster than Dimension RTs. Left RLPFC was specifically engaged when relational integration was required, whereas right RLPFC was more generally engaged as a function of relational task demands.
