Figure 4.
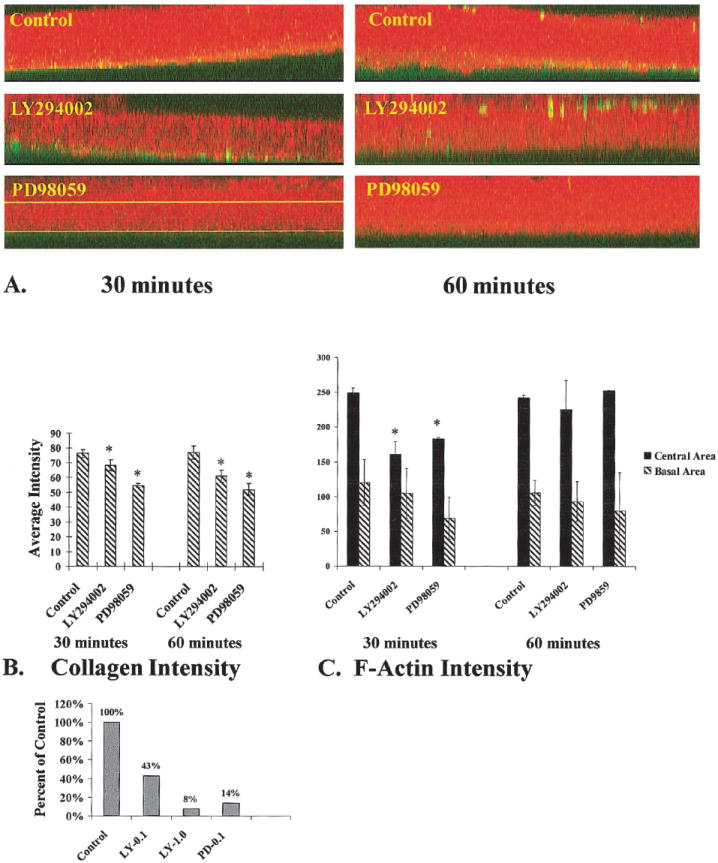
COL binding and F-actin accumulation in the presence of MAP kinase or PI-3 kinase inhibitors. Epithelia were cultured in the presence and absence of either MAP kinase (100 μM PD98059) or PI-3 kinase inhibitor (100 nM LY294002) and stimulated with FITC-labeled COL for 30 or 60 minutes. A complete z-series of confocal images were projected into one image. Then an xz image was produced from the projected three-dimensional stack (A). These final images contained all the image pixels from the complete set of z-series images. Average intensities (scale range, 0–255) of bound COL (green) and F-actin (red) were determined using a line drawn through the center of the basal cells (upper line in A, PD98059 tissue) or at the base of the epithelia (lower line in A, PD98059-treated tissue). Densitometry software was used to determine average intensities of bound COL (green channel intensity levels, n = 4 epithelia per group) cellular F-actin (red channel intensity levels, n = 4 epitheliaper group). In the basal compartment, there was a decrease in both bound COL (B, *P ≤ 0.05) and F-actin (C) in PI-3 kinase– and MAP kinase–inhibited epithelia compared with control epithelia. The actin accumulation in the center of the basal cells also demonstrated a marked difference between groups at 30 minutes (C, *P < 0.05). However, by 60 minutes, there was no difference between groups (C). Collagen-coated polystyrene beads were used to further quantitate the differences in collagen binding (D). The tissues were incubated basal side up and treated with inhibitors, and the collagen-coated beads were added to the medium for 30 minutes. The tissues were placed in a black 96-well dish (1 epithelium per well; n = 5–10 epithelia per treatment group) and analyzed with a fluorometer. The intensity of each well was analyzed with both FITC and rhodamine filter sets. The mean intensity and SDs were calculated for each group. Tissue treated with 100 nM LY294002 had 43% intensity compared with controls, whereas tissues treated with 1 μM LY294002 had less than 10% intensity. Tissues treated with 100 μM PD98059 had 14% of control intensity.
