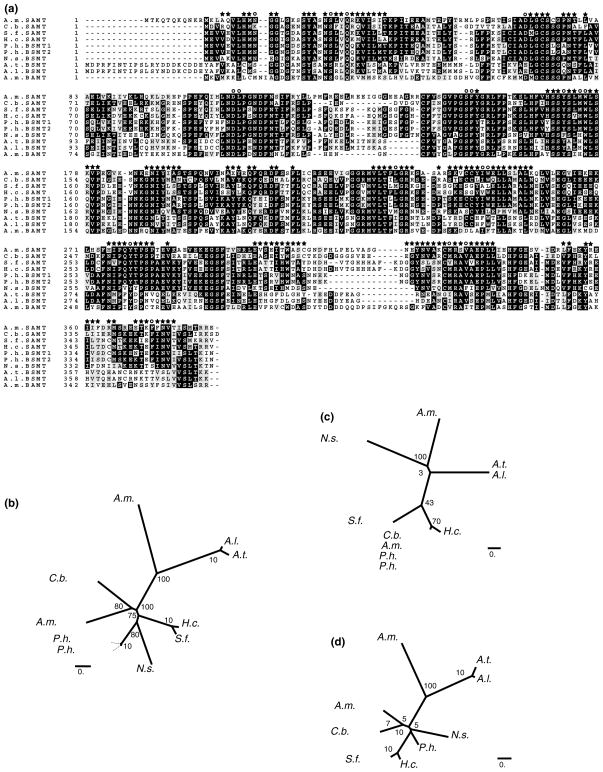
Fig. 1.
Phylogenetic trees of carboxyl methyltransferases based on computer modelling. (a) Alignment of amino acid sequences of 10 carboxyl methyltransferase. Alignment was performed using AlignX. The circle symbol indicates amino acids of the binding pocket (see Table 4), and the star symbol indicates amino acids of the 2nd tier. (b) Unrooted neighbor-joining phylogenetic tree based on amino acid sequence similarity between plant benzenoid carboxyl methyltransferases complete amino acid sequences (355 to 392 amino acids). (c) Unrooted neighbor-joining tree based on amino acids involved in the methyl acceptor binding pocket of plant benzenoid carboxyl methyltransferases (amino acids presented in Table 4). (d) Unrooted neighbor-joining tree based on 2nd tier amino acids which were found in clusters within a 10 Å radius around each of the residues in the methyl acceptor binding pocket. The unrooted neighbor joining trees and associated bootstrap values were generated using the PHYLIP software package (Felsenstein, 1985). TreeView was used to visualize the resulting trees. The accession No. of the Hoya carnosa SAMT is AJ 863118.