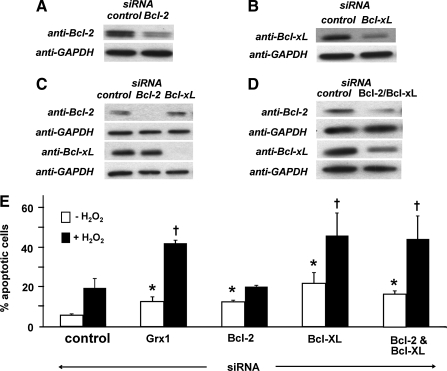
FIG. 9.
Effect of Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL knockdown on apoptotic susceptibility in H9c2 cells. (A) Content of Bcl-2 was diminished via transfection with targeted siRNA as described in Materials and Methods. Representative Western blot analysis of Bcl-2 content in control and Bcl-2 knockdown H9c2 cells (knockdown = 63 ± 4%, n = 3). (B) Content of Bcl-xL was diminished via transfection with targeted siRNA as described in Materials and Methods. Representative Western blot analysis of Bcl-xL in control and Bcl-xL knockdown H9c2 cells (knockdown = 45 ± 7%, n = 6). (C) Complete knockdown of Bcl-2 or Bcl-xL does not affect expression of the other protein. H9c2 cells were treated with sufficient concentrations of Bcl-2- or Bcl-xL-targeted siRNA to reduce the target protein to undetectable levels, and content of each protein was determined by Western blotting. Bcl-2 content in Bcl-xL knockdown cells were 116 ± 13% (mean ± SEM) of the value in control cells (n = 9). Bcl-xL content in Bcl-2 knockdown cells was 97 ± 10% (mean ± SEM) of the value in control cells (n = 4). (D) Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL content were both diminished via transfection with targeted siRNA. Representative Western blot showing ∼40% simultaneous knockdown of both Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL in H9c2 cells (Bcl-2 knockdown: 45 ± 3%; Bcl-xL knockdown: 37 ± 6%, n = 6). (E) Apoptosis in control, Bcl-2 knockdown, Bcl-xL knockdown, and Bcl-2/Bcl-xL double knockdown cells ± H2O2 treatment (400 μM for 5 min, followed by 24 h recovery, see Materials and Methods). Open bars (□), no treatment; closed bars (▪), H2O2. Data represent mean % apoptotic cells ± SEM (n = 3–10). *p < 0.05 vs. control siRNA (without H2O2); †p < 0.05 vs. control siRNA (with H2O2).