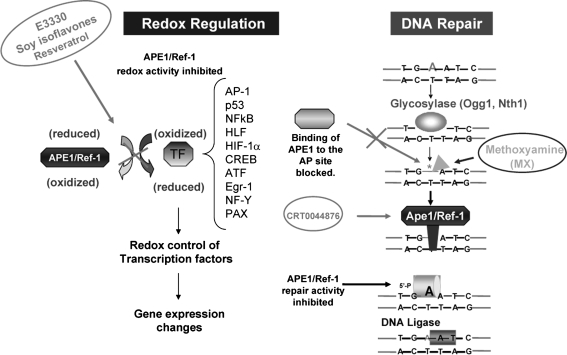
FIG. 6.
APE1 has dual roles in redox and DNA repair. APE1 possesses two major functions: redox regulatory/signaling and DNA repair. Through its redox function, APE1 regulates gene expression by modifying the redox status of some transcription factors involved in variety of cancer processes. Small molecules that block APE1 redox function are shown in ovals. In addition to its redox function, APE1 plays a critical role in the BER DNA-repair pathway as an AP endonuclease, which processes the AP sites. Blocking AP sites by using methoxyamine (MX) or APE1 or both directly by using APE1-specific inhibitors such as CRT0044876 may decrease DNA repair and lead to tumor-cell death. [Adapted from Luo et al. (128).]