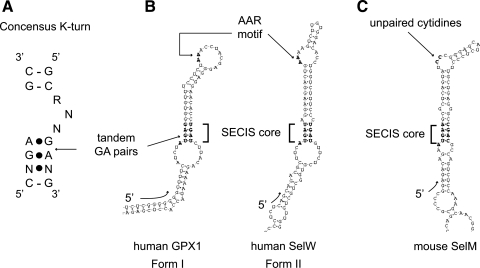
FIG. 1.
Comparison of K-turn and SECIS elements. (A) The consensus K-turn as described (34). The canonical Watson–Crick base-paired stem is separated from the noncanonical, sheared tandem GA pairs containing, stem. Base pairing marked by dots indicate non-Watson–Crick interactions. (B) Canonical form I and form II SECIS elements are depicted here by the human GPX1 and SelW SECIS elements, respectively. The SECIS core and AAR motifs are in shown in bold and indicated by brackets and arrows. (C) The mouse SelM SECIS element with apical unpaired cytidines is shown for comparison with the canonical SECIS elements in (B). SECIS elements were drawn with the SECISearch program (37) and orientation of the RNAs is indicated by the 5′ arrow at the base of the SECIS elements.