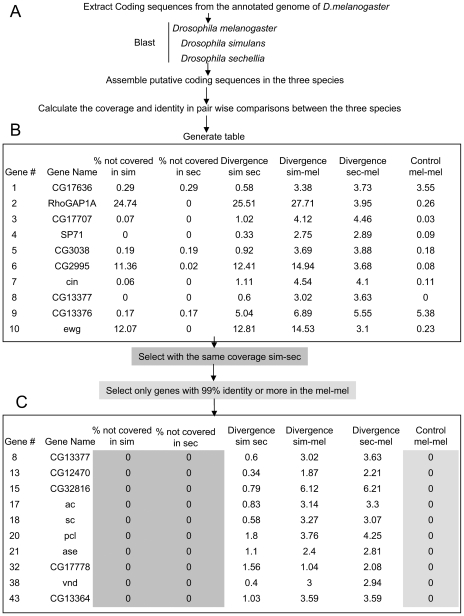
Figure 1. Overview of the data collection and sorting.
A) Exons of coding sequence were extracted from the annotated genome of D. melanogaster using Extractor and electronically joined using Analyst to obtain complete coding sequences. These coding sequences were then automatically blasted against the genome of D. melanogaster, D. simulans and D. sechellia with Megablast. Analyst scanned the resulting alignments for the best hits and assembled the coding sequences in the three species from them. B) Analyst also calculated the coverage, the percentage not covered, the divergence in sim-sec, sim-mel, sec-mel as well as the control mel-mel and organized this data in a table. C) To minimize artifacts due to incomplete clone representation in the genomic libraries, the coding sequences were filtered and only genes with the same coverage in D. simulans and D. sechellia retrieved. To avoid genes truncated by Megablast (i.e. usually genes with small exons), only genes with a mismatch up to 1% in the control mel-mel were retrieved. After these two filters were applied, a new table like the one exemplified in C) was generated for each chromosome.