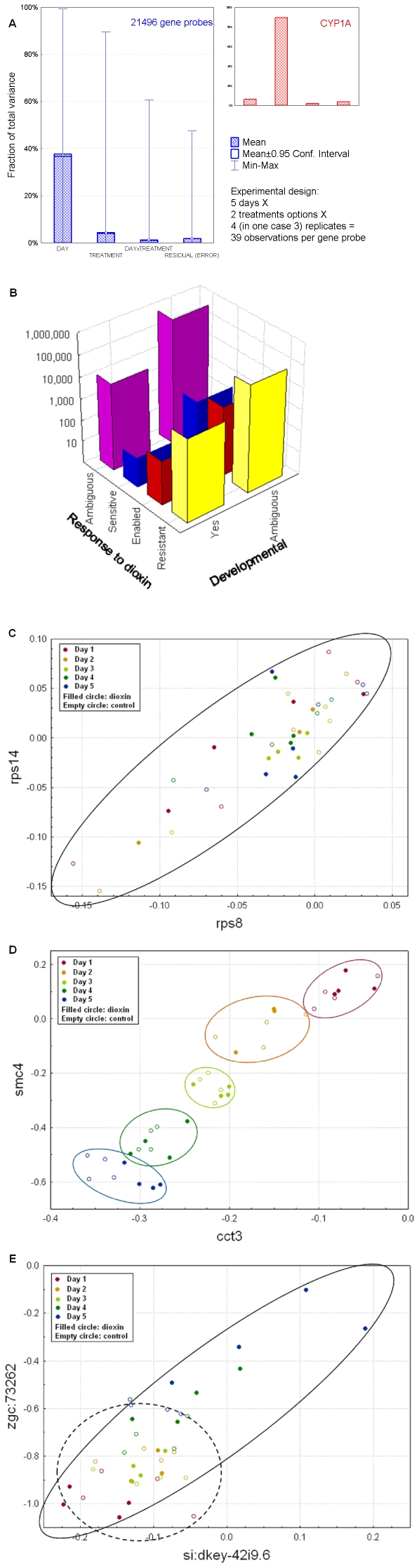
Figure 2. Experimental factors affecting differentially-expressed genes (A), occurrence of different kinds of differentially-expressed links (B), and examples of types of links (C–E).
A. Fraction of variance [92] of transcriptional change for the whole set of analyzed transcripts (blue) and for cyp1a (red), associated with different experimental factors. While developmental changes dominated, dioxin modulated as many as 2009 genes at one or more time points in the experiment (detected by 2-way ANOVA on factors “DAY” and “TREATMENT”, applied to individual genes). 95% confidence intervals are too small to be seen in most cases. cyp1a regulation was largely treatment-dependent (the horizontal legends are identical to the whole set chart). B. Distribution of specific functional links inferred in the FunCoup network by analysis of microarray data. We discovered dioxin-enabled, dioxin-sensitive, and dioxin-resistant links, along with developmental stage-specific links. The majority of FunCoup links did not overlap with any of these categories, either because a gene was absent from the microarray chip, or because its transcription was not perturbed in the experimental conditions. The number of dioxin-sensitive links is smaller than the number of dioxin-enabled links, and both are much smaller than the number of dioxin-resistant links. Differentially expressed links were detected here via ANOVA (combined with Pearson correlation metric) by considering a third factor “GENE” and its interaction with “DAY” and “TREATMENT”. Note the logarithmic scale of the vertical axis. C, D, E. Visualization of specific link types. All 3 gene pairs were significantly co-expressed (PLC equaled 0.876, 0.946, and 0.754, respectively). Plot axes indicate relative transcript abundance of the genes (log10 ratio of the experimental value to the transcript abundance in the reference pool). C. For this correlation, the condition- and day-specific points were mixed randomly. The reason for the high co-expression of the two genes (both of which code for ribosomal proteins) was probably not associated with the parameters examined in our experiment, and this link would be characterized as “Ambiguous” rather than “Developmental” or dioxin-altered. D. The transcript levels for these two genes (coding for proteins involved in chromosome maintenance and protein folding) were strongly synchronized according to day, so the link was classified as “Developmental.” E. Co-expression was observed under the dioxin treatment, but absent in the control (PLC 0.9032 and 0.1286, respectively), so the link was classified as “dioxin-enabled”. These genes are uncharacterized—but now known to lose functional coupling after dioxin exposure. The differentiation between C, D, and E would not be possible without deeper variance decomposition in ANOVA. See Methods S1 for details.