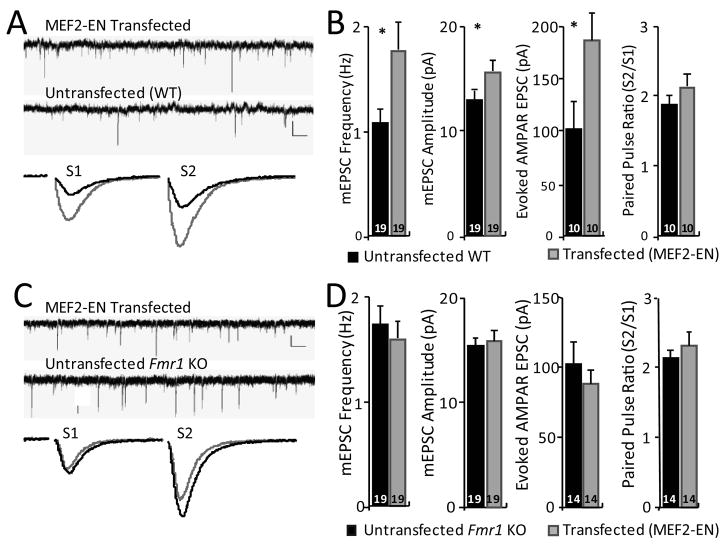
Figure 2. Inhibition of endogenous MEF2 function enhances synapse number in wildtype, but not in Fmr1 KO neurons.
A, Representative traces of mEPSCs (upper; scale bar = 10 pA/500 ms.) and evoked EPSCs (lower; scale bar = 50 pA/10 ms) from a simultaneous recording from an untransfected and neighboring MEF2-Engrailed (MEF2-EN) transfected WT neuron. B. Average mEPSC frequency, mEPSC amplitude, evoked EPSC amplitude, and paired-pulse ratio from untransfected WT and MEF2-EN transfected cells. Averages are plotted + SEM and n (# of cell pairs) is indicated on each bar. * p< 0.05. C, D MEF2-EN transfection into Fmr1 KO slice cultures. C. Representative traces of mEPSCs (upper; scale bar = 10 pA/500 ms.) and evoked EPSCs (lower; scale bar = 50 pA/10 ms) from a simultaneous recording of an untransfected and neighboring MEF2-EN transfected Fmr1 KO neuron. D. Average mEPSC frequency, mEPSC amplitude, evoked EPSC amplitude, and paired-pulse ratio from untransfected and MEF2-EN transfected Fmr1 KO neurons.