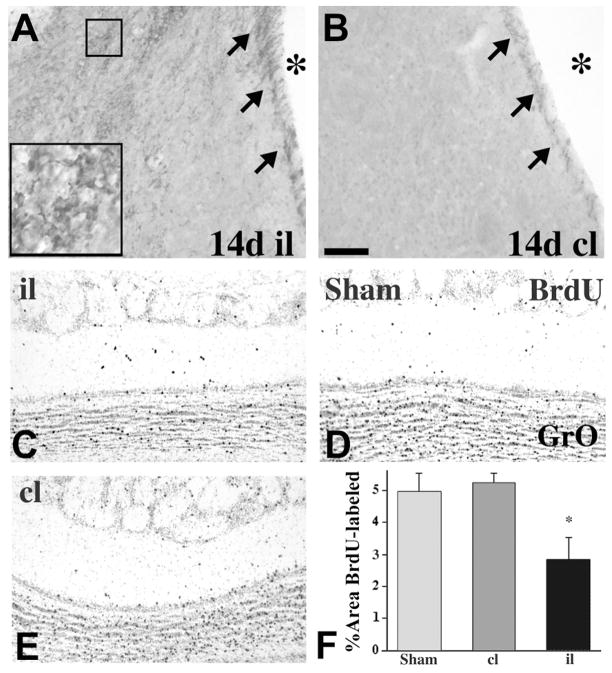
Figure 2.
Stroke-induced neurogenesis. A, B, Doublecortin immunostaining at 14 days after tMCAO shows increased SVZ and striatal neurogenesis of the ipsilateral (il) hemisphere compared to contralateral (cl). The asterisks denote the lateral ventricle. C–E, Coronal sections of BrdU-immunoreactive olfactory neurons in the granular layer (GrO) of rats after tMCAO either ipsilateral (il, C) or contralateral (cl, D) to the infarct, or from a sham-operated control (E) at 28 days after surgery. (D) Quantification of GrO BrdU labeling shows significantly decreased BrdU-immunoreactivity il to the stroke after 28 days. *, p < 0.05 vs. cl and sham control. Scale bar, 50 μm for A and B; 150 μm for C–E.