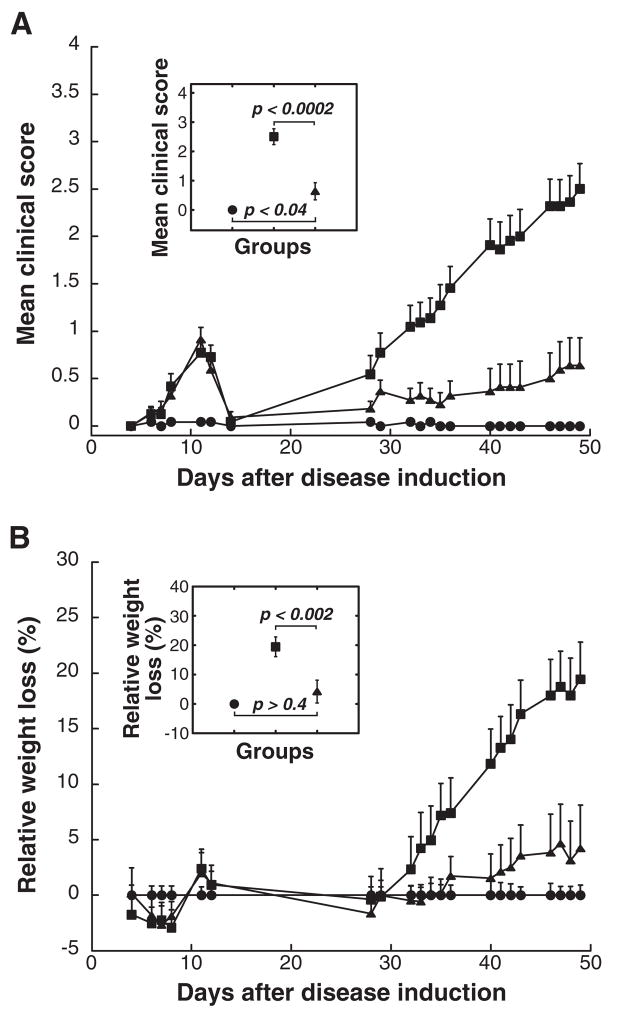
Figure 1. EAMG was substantially suppressed in rats treated i.p. with 5 mg doses of a mixture of human α1, β1, γ, δ, and ε subunits at weekly intervals starting on day 14 following disease induction.
All rats, except adjuvant control (closed circles) which received only adjuvant, were immunized with 35 μg of Torpedo californica AChR in TiterMax adjuvant at day 0. Treatments (i.p., 5 mg/dose) were initiated after the acute phase, 14 days after EAMG induction, and thereafter once a week for 5 weeks until the end of the experiments. The EAMG control rats received no treatment (closed squares). Data represent the mean ± SE of two independent experiments (n = 12 for each point, from 6 rat groups in each of two experiments). (A) The mean clinical scores of the rats treated with the subunit mixture (closed triangles) were significantly lower when compared to those of the EAMG control rats (closed squares) at all time points after day 30 (p < 0.01). (B) The effect of the treatment on clinical symptoms was corroborated by changes in the rats’ body weight. Relative weight loss was calculated as follows: % relative weight loss = 100 − (body weight on day X/average body weight of adjuvant control on day X) × 100. The insert indicates the statistical significance of the difference between groups on day 49 by the t-test.