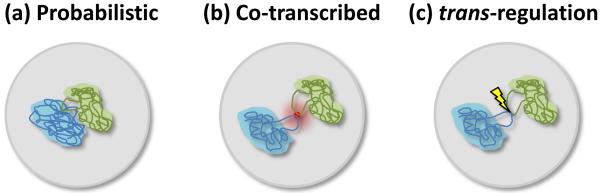
Figure 5.
Three types of Interchromosomal association. (a) Positioning of loci is probabilistic, determined by the sum of properties of neighboring sequences and the chromosome as a whole. Associations have no obvious functional significance. (b) Co-transcribed genes coalesce in and around nuclear bodies such as transcription factories and splicing speckles. As such bodies might be specialized in transcribing similar genes, these associations could help in coordinating gene expression and increase efficiency of transcription. Alternatively, these associations may be probabilistic as in (a) and have no functional significance. (c) Sequences regulate gene expression in trans through interchromosomal contacts.