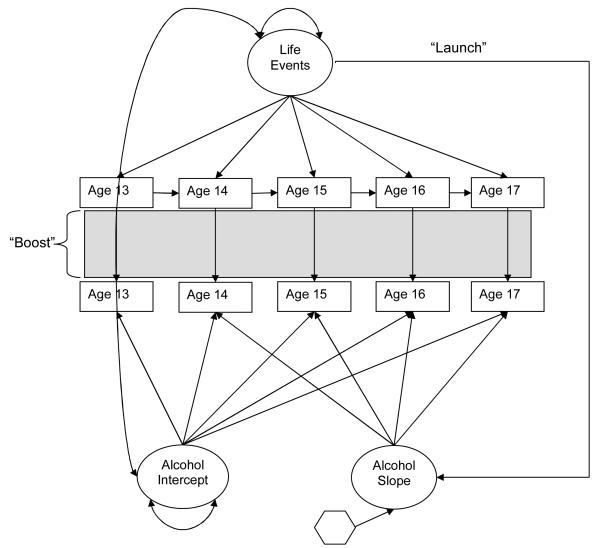
Figure 2. The Unconditional Parallel Models of State-Trait Family Stressors and Growth in Drinking Across Adolescence.
This structural model illustrates the association between the parallel models of growth in drinking and state-trait family stressors. The “boost” hypothesis is tested in the effects of residualized stressors at each time point on residualized alcohol use at each time point. The “launch” hypothesis is tested by examining the effect of trait stressors on growth in alcohol use, and the “marker” hypothesis is tested by examining how much that effect is reduced by the addition of shared risk factors.