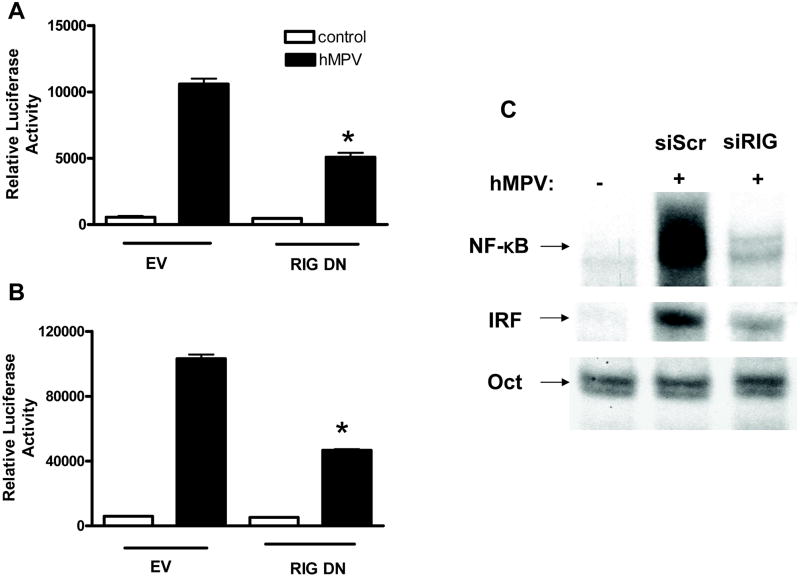
Fig. 4. Effect of RIG-I inhibition on hMPV-induced NF-κB and IRF activation.
A549 cells or 293 cells were cotransfected with a luciferase reporter plasmid containing multimers of the RANTES ISRE site (A) or IL-8 NF-κB site (B) together with a RIG-I DN expression plasmid or an empty vector (EV). Cells were infected with hMPV and harvested at 15 h p.i. to measure luciferase activity. Uninfected plates served as controls. For each plate luciferase was normalized to the β-galactosidase reporter activity. Data are expressed as mean ± standard deviation of normalized luciferase activity. Bars represent the mean value of triplicate samples of one experiment, n = at least two experiments. *, P< 0.05 relative to hMPV-infected EV-treated cells. (C) A549 cells were transfected with scrambled siRNA (siSCR) or specific siRNA against RIG-I (siRIG) and mock infected or infected with hMPV for 15 h. Nuclear extracts were harvested and subjected to EMSA with 32P-labeled oligonucleotide probes corresponding to the IL-8 promoter NF-kB site, the RANTES promoter ISRE site or an Oct synthetic probe. Results are representative of two separate experiments.