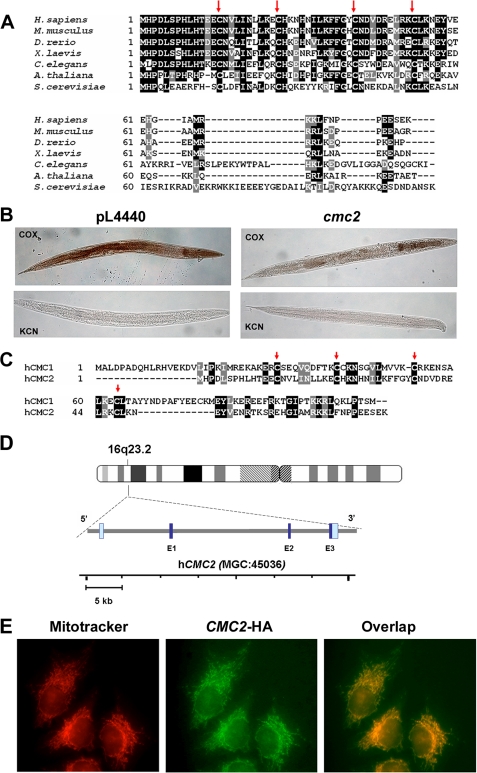
FIGURE 6.
Properties and expression of metazoans homologues of yeast CMC2. A, CMC2 is conserved across kingdoms, from yeast to human. Sequence alignment of S. cerevisiae CMC2 homologues from human (Homo sapiens), fish (Danio rerio), frog (Xenopus laevis), fruit fly (Drosophila melanogaster), worm (C. elegans), and plant (Arabidopsis thaliana). Red arrows indicate conserved cysteine residues. B, histochemical staining for cytochrome c oxidase activity in cmc2-silenced C. elegans. Worms fed HT115DE(3) bacteria transformed with empty vector pL4440 were used as negative controls. Silenced (cmc2) and control (pL4440) rrf-3(pk1426) nematodes were fixed, permeabilized, and stained for COX. Control reactions contained the COX-specific inhibitor KCN. Photographs of representative examples of the whole controls and silenced nematodes are shown. C, sequence alignment of human CMC1 and CMC2 proteins. D, localization and genomic structure of the human hCMC2 gene based on the result of a BLAST search of the human genome for homology to the hCMC2 cDNA sequence. The dark blue and gray bars depict the exon and intron regions, respectively. E, subcellular localization of CMC2 in human HeLa cells. Cells were transiently transfected with a cDNA coding for a hemagglutinin-tagged CMC2. The protein was visualized by indirect immunofluorescence using Mitotracker Red and a fluorescently conjugated antibody to human to the hemagglutinin epitope of CMC2-HA (green). A merged image is shown on the right.