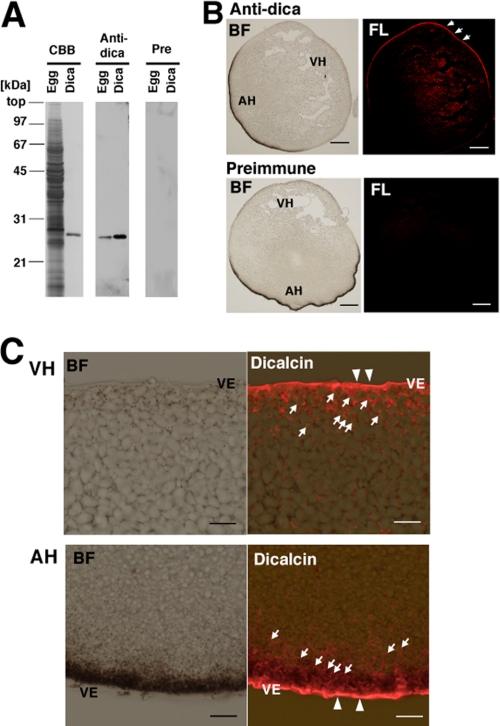
FIGURE 2.
Localization of dicalcin in Xenopus eggs. A, specificity of anti-dicalcin antibody. Left (CBB): CBB staining of the proteins after SDS-PAGE of the homogenate of Xenopus eggs (Egg) and recombinant dicalcin (Dica). Middle (Anti-dica): Western blot analysis of homogenates of Xenopus eggs (Egg) and recombinant dicalcin (Dica) treated with anti-dicalcin antibody. Right (Pre): Blots treated with preimmune antibody. B, immunohistochemical staining at a low magnification. Eggs were fixed, and serial sections (∼14-μm thickness) were treated with anti-dicalcin antibody (Anti-dica) or preimmune antibody (Preimmune). Dicalcin is localized in the marginal area of Xenopus eggs (arrows). BF, bright field observation; FL, fluorescence image. Anti-dica, stained with anti-dicalcin antibody; Preimmune, stained with preimmune antibody. Scale bar: 200 μm. C, detailed localization of dicalcin in Xenopus eggs. Dicalcin is localized in the extracellular vitelline envelope (arrowheads) and in the cytosolic cortex of the egg (arrows). BF, bright field observation; Dicalcin, merged image of bright field and fluorescence image stained with anti-dicalcin antibody. VH, vegetal hemisphere; AH, animal hemisphere; and VE, vitelline envelope. Scale bar: 20 μm.