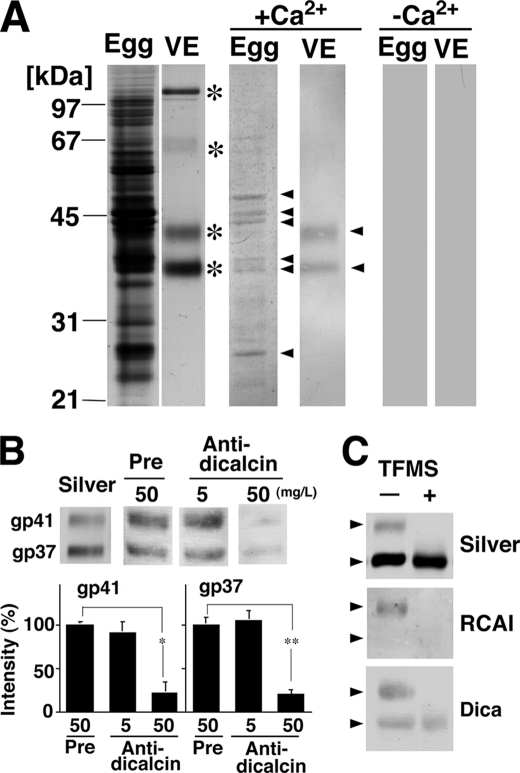
FIGURE 3.
Ca2+-dependent binding of dicalcin to protein cores of gp41 and gp37. A, dicalcin binds to several egg and VE proteins. Soluble egg proteins and vitelline envelope (VE) proteins were prepared as stated under “Experimental Procedures.” VE proteins are composed of four major proteins (asterisks). Blots of both egg-soluble proteins and VE proteins were probed by biotinylated dicalcin either in the presence or absence of Ca2+. Dicalcin bound to several egg proteins and two VE proteins (gp41 and gp37) in the presence of Ca2+ (arrowheads), but not in the absence of Ca2+. Egg, soluble egg proteins; VE, VE proteins. +Ca2+, blot overlay analysis in the presence of Ca2+ (500 μm CaCl2); −Ca2+, analysis in the absence of Ca2+ (500 μm EGTA). B, anti-dicalcin antibody inhibits the binding of dicalcin to gp41 and gp37. Blots of VE proteins were probed with biotinylated dicalcin either in the presence of anti-dicalcin antibody (Anti-dicalcin; 5 and 50 mg/liter) or preimmune antibody (Pre; 50 mg/liter). Silver, silver-stained VE proteins after SDS-PAGE; Pre, blot overlay analysis treated with preimmune antibody; Anti-dicalcin, blot overlay analysis treated with anti-dicalcin antibody. The graph shows mean data (n = 6; *, p = 0.0015; **, p = 2.4 × 10−5). C, dicalcin binds to deglycosylated forms of gp41 and gp37. VE proteins were treated with TFMS for 3 h. Blots of glycosylated and deglycosylated proteins were probed either with fluorescently labeled RCAI or biotinylated dicalcin. Silver, silver-stained proteins treated with TFMS (TFMS +) or without treatment (TFMS −); RCAI, blot with RCAI; Dica, blot with biotinylated dicalcin. Arrowheads indicate the positions of gp41 and gp37.