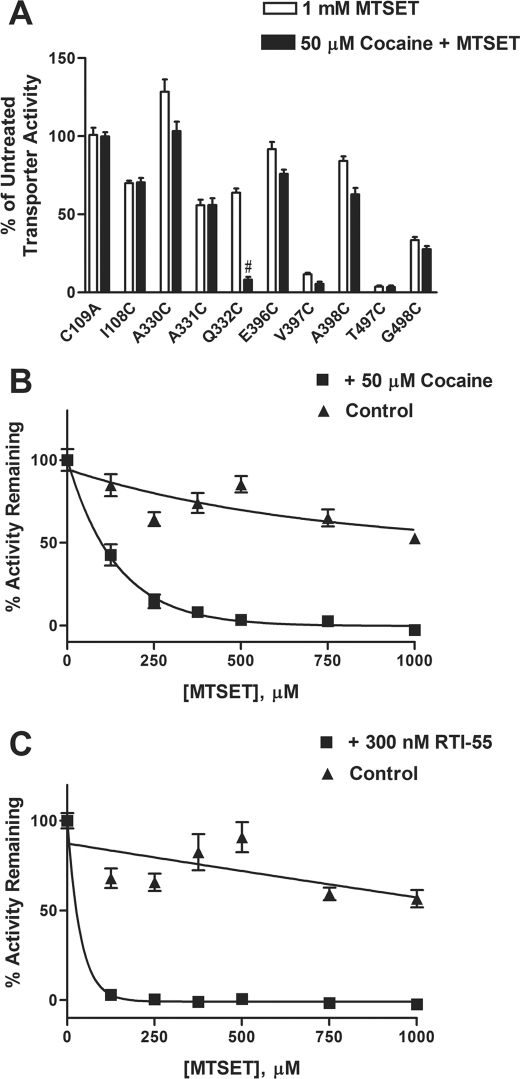
FIGURE 6.
Effect of cocaine on reactivity of hSERT Q332C mutant with MTSET. A, the ability of the hSERT antagonist cocaine to alter the reactivity of hSERT Cys mutants to MTSET was assessed in HEK-293 cells transiently transfected with each Cys mutant. The cells were incubated with buffer or 50 μm cocaine for 5 min at room temperature, followed by incubation in the presence or absence of 1 mm MTSET for 10 min. After washing, [3H]5-HT uptake assays were performed as described under “Experimental Procedures.” Bars, mean ± S.E. (error bars) from three independent experiments performed in triplicate. The data were normalized to the total uptake of each individual mutant. #, p < 0.001 versus MTSET treatment using a one-way analysis of variance with Bonferroni's post hoc test. The effect of cocaine on the rate of MTSET inactivation was determined in HEK-293 cells transiently transfected with the cDNA for the Q332C mutant. The cells were incubated with increasing concentrations of MTSET in the presence (filled squares) or absence (filled triangles) of 50 μm cocaine (B) or 300 nm RTI-55 (C), a cocaine analog, followed by determining [3H]5-HT uptake, as described under “Experimental Procedures.” The nonspecific uptake was determined using 10 μm fluoxetine. MTSET inactivated Q332C at an estimated rate of ∼700 m −1 min−1 versus ∼140 m−1 min−1 in the presence or absence of cocaine, respectively. MTSET inactivated Q332C at a calculated rate of ∼2600 m−1 min−1 in the presence of RTI-55, which is estimated to be significantly greater than a rate that causes complete inactivation at ∼125 μm under the conditions used. Data represent the mean from three independent experiments performed in triplicate.