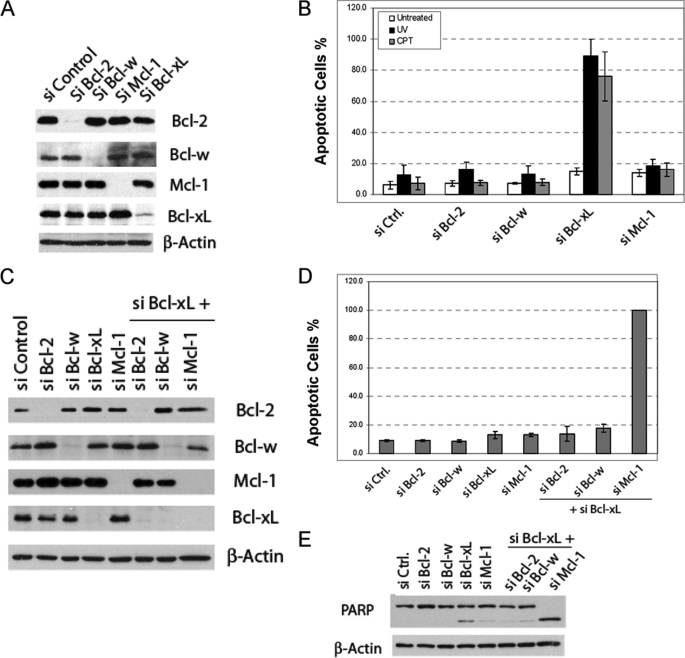
FIGURE 1.
Identification of anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 proteins critical for inhibiting apoptosis induced by DNA damage in HeLa cells. A, knockdown of the anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 proteins by siRNA is shown. HeLa cells were transfected with the indicated pools of siRNA duplexes. After siRNA transfection, cell lysates were generated and subjected to Western blot analysis. B, effects of siRNA knockdown on DNA damage-induced apoptosis in HeLa cells are shown. After siRNA transfection, HeLa cells were treated with either CPT (75 μm) or UV (20 J/m2). Three hours later, apoptosis was quantified by Hoechst staining. The results are the mean ± S.D. of at least three independent siRNA transfections. These same doses were used in all the subsequent experiments involving CPT and UV. C, combinatorial siRNA knockdown of Bcl-xL and other anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 proteins detected by Western blot is shown. D, effects of the combinatorial siRNA knockdown on the apoptosis of HeLa cells are shown. Forty-eight hours after siRNA transfection, apoptosis was quantified by Hoechst staining. The results are the mean ± S.D. from at least three independent siRNA transfections. The apoptosis after knockdown of Mcl-1 and Bcl-xL was 100% in each experiment. E, PARP cleavage induced by Mcl-1 and Bcl-xL double knockdown was assayed by Western blot analysis of the whole cell lysates using PARP antibody. Ctrl, control.