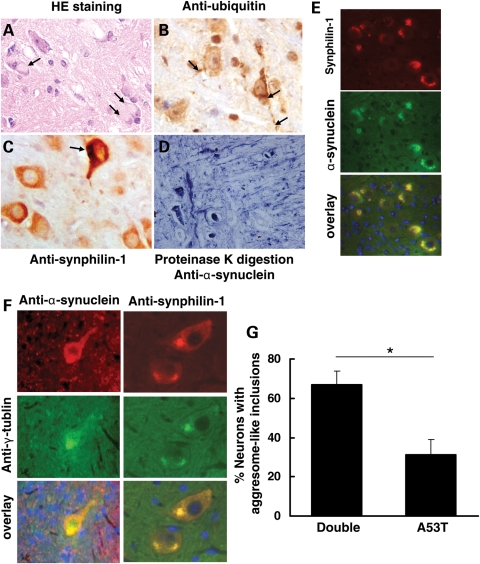
Figure 4.
Synphilin-1 promoted aggresome-like inclusion formation in double-transgenic mice at end-stage disease. (A) Sagittal mouse brain sections were subjected to hematoxylin and eosin (HE) staining, immunostaining with DAB detection using anti-ubiquitin (B) and anti-synphilin-1 (C) antibodies, proteinase K digestion followed by anti-α-synuclein staining (D), double-immunostaining using anti-α-synuclein and anti-synphilin-1 antibodies (E). (A) Eosinophilic cytoplasmic inclusions (arrow) in the pons in sick double-transgenic mice by HE staining. (B) Ubiquitin pathology in sick double-transgenic mice. Pathological somal and neuritic (arrow) accumulation of ubiquitin was prominent in pons. (C) Synphilin-1 was highly expressed in neurons in pons in sick double-transgenic mice. Arrow showing the synphilin-1-positive inclusions. (D) Brain sections from double transgenic mice over digested with proteinase for 3 h and then followed by immunostaining using anti-α-synuclein antibodies. The representative image showing the abnormal accumlation of α-synuclein in pons in sick double-transgenic mice (11 months). (E) Inclusions in double-transgenic mice labeled using anti-α-synuclein and anti-synphilin-1antibodies. Red, α-synuclein; green or synphilin-1 staining; DAPI staining for nuclei. (F) Aggresome-like inclusions in double-transgenic mice. Red, α-synuclein (left) or synphilin-1 (right) staining; green, γ-tublin staining; DAPI staining for nuclei. (G) Graph showing the quantification of neurons in brainstem with inclusions that were positively stained with both anti-α-synuclein and anti-γ-tublin antibodies, which resembled aggresome-like structures. P < 0.05 by Student's t-test.