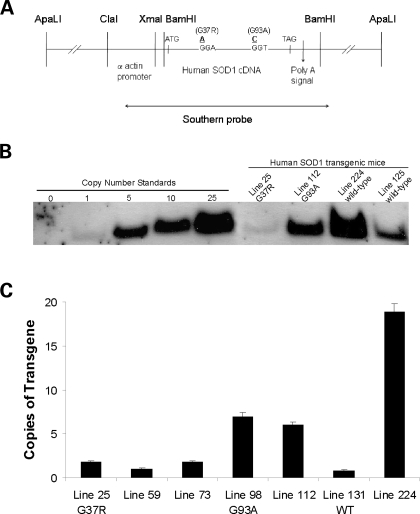
Figure 1.
Design of hSOD1mus gene constructs and generation of tg mice. (A) Schematic representation of constructs used in creating hSOD1mus mice. The skeletal muscle-specific α-actin promoter was used to drive expression of human wild-type or mSOD1. The human wild-type cDNA is shown. Two different point mutations were introduced by site-specific mutagenesis to convert codon 37 from a glycine to an agrinine or codon 93 from a glycine to an alanine. The probe used for Southern analysis spanned the entire chicken αsk actin promoter and coding region of hSOD1. (B) Southern blot analysis of hSOD1mus transgene copy number in different tg mouse lines. NcoI digestion of mouse tail genomic DNA yields a 2.5 kb fragment in tg mice. Positive controls/copy number standards were digested tail DNA from non-tg mice spiked with various amounts of ApaLI-digested construct. The negative control (0) was non-spiked DNA from non-tg mice. (C) qPCR analysis of hSOD1 transgene copy number in representative hSOD1mus tg G37R mice (lines 25, 59 and 73), G93A mice (lines 98 and 112) and wild-type mice (lines 131 and 224). Bars represent mean ± SEM and are the results of triplicate experiments.