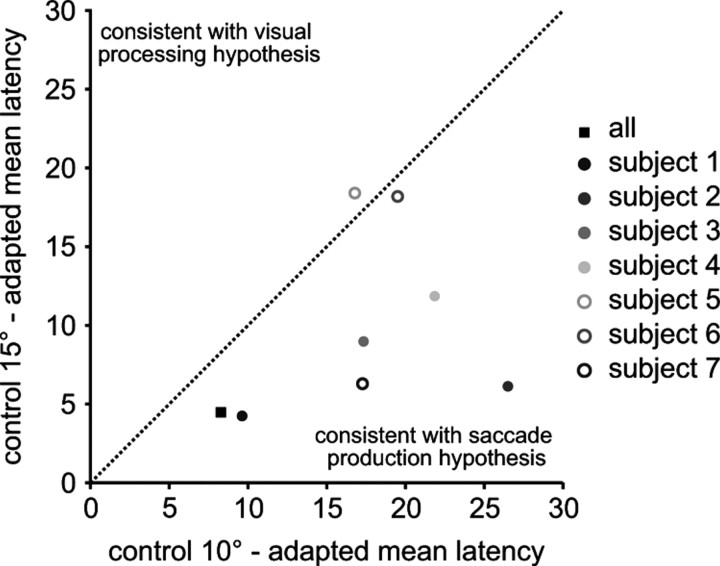
Figure 4.
Direct comparison between motor and visual hypotheses. The x-axis plots the mean absolute difference between the average adapted saccade latencies and the average 10° control latencies. The differences between the mean latencies at each cue location were calculated and then all 7 differences were averaged. The y-axis plots the mean absolute difference between the average adapted saccade latencies and the average 15° control latencies. Each dot represents one subject and the black filled square represents the mean difference from all subjects. The diagonal line represents unity. A data point below the line is consistent with the motor production hypothesis because the difference between the adapted saccade and the 10° control target latencies are smaller than the difference between the adapted saccade the 15° control target latencies. A data point above the line of unity is consisted with the visual processing hypothesis.