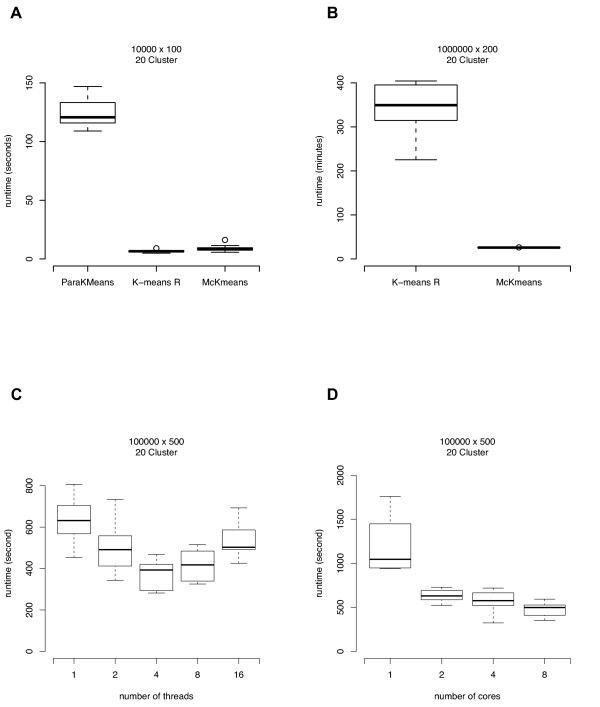
Figure 5.
Runtime performance of ParaKMeans, k-means R, and McKmeans on the artificial data sets. Benchmark results for the simulated data sets (no cluster structure imposed, features chosen uniformly from [0, 1]) comparing the runtime of ParaKMeans, k-means R, and McKmeans. For the smaller data set (panel A) the computational overhead of the parallelization negatively affects the runtime. For the larger data set (1 million cases, panel B) an improvement of the runtime by a factor of 10 can be observed. The network-based parallelization algorithm ParaKMeans is significantly slower than McKmeans. Panel C shows the dependency of the runtime on the number of threads used (Kruskal-Wallis test: p = 1.15 × 10-5) and Panel D the number of cores used (Kruskal-Wallis test: p = 4.59 × 10-6) for a data set of 100000 cases and 500 features. Each box summarizes the results from 10 repeated clusterings (median and interquartile range).