Fig. 7.
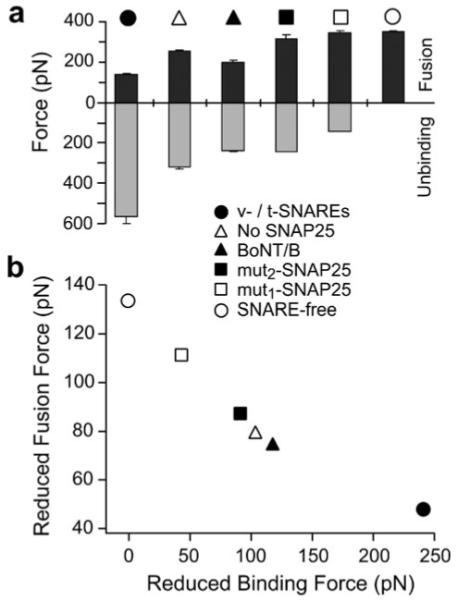
Facilitation of membrane fusion is coupled to the pulling strength of interacting SNAREs in the opposite bilayers. (a) Fusion forces (black) were derived from the DFS (see Fig. 2 and 3) at a compression rate of 20 000 pN s−1 in the compression experiments under the specified experimental conditions. The unbinding force measurements (gray) were derived from the DFS (see Fig. 5) at loading rate of 20 000 pN s−1 in the unbinding experiments under the same conditions. It is evident that an inverse relationship between the fusion force and the SNARE unbinding force exists under these conditions. Error bars are the s.e.m. of either the fusion or the unbinding forces measured at the compression/loading rate of 20 000 pN s−1, respectively. (b) Membrane fusion facilitation quantified by the reduced fusion force (fϕ) correlates with the pulling force of interacting SNAREs as characterized by the reduced unbinding force (fβ). This reveals that the pulling force generated by interacting SNAREs facilitates membrane fusion in a force dependent manner.
