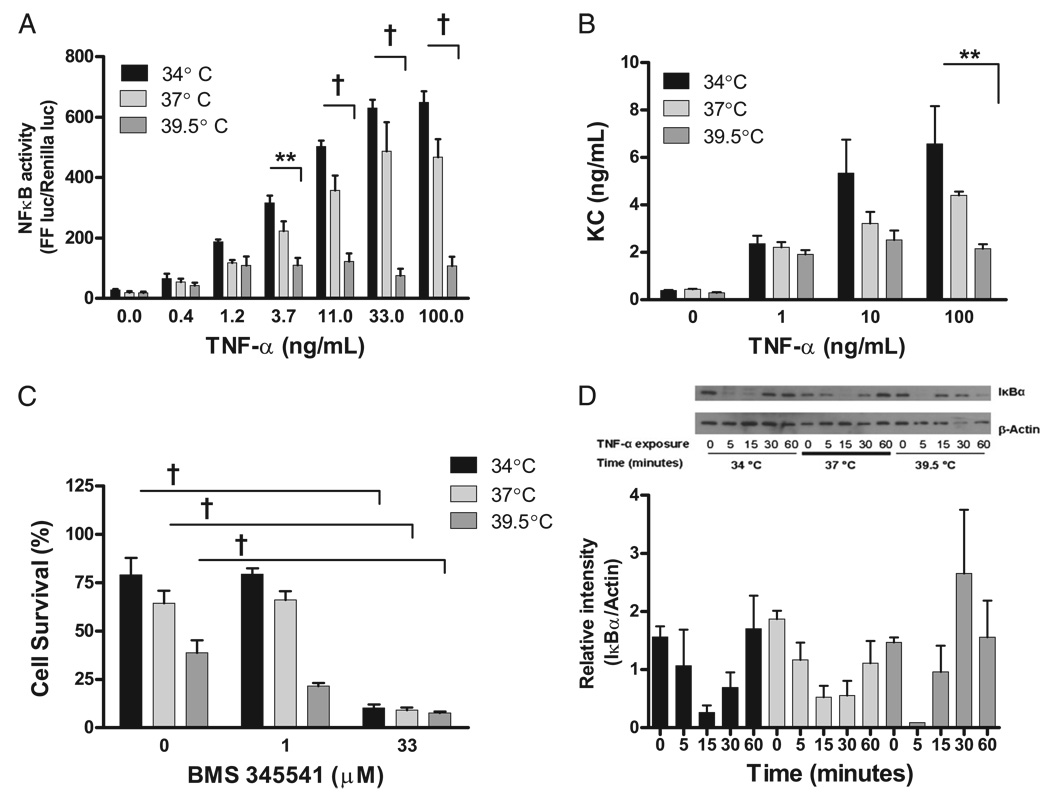
FIGURE 12.
FRH suppresses NF-κB activity, which increases MLE-15 susceptibility to TNF-α–mediated death. A, MLE-15 cells were transiently dually transfected with an NF-κB–inducible firefly luciferase and a constitutively active renilla luciferase and then exposed to TNF-α at 34, 37, or 39.5°C. NF-κB activity in MLE-15 cells generated by TNF-α exposure is strongly suppressed as a function of increasing incubation temperature. B, KC production from MLE-15 cells after TNF-α exposure is suppressed by increasing incubation temperatures. C, The IκB-α kinase inhibitor BMS 345541 renders the MLE-15 cells at all incubation temperatures more sensitive to TNF-α–mediated cell death. In the absence of TNF-α, the IκB-α kinase inhibitor does not affect cell viability (data not shown). D, Total IκB-α levels in MLE-15 cells exposed to TNF-α 50 ng/ml fluctuate similarly in all temperature exposures. A representative Western blot is shown with densitometry from three Western blots for total IκB-α normalized for protein loading. **p< 0.01; †p< 0.001.