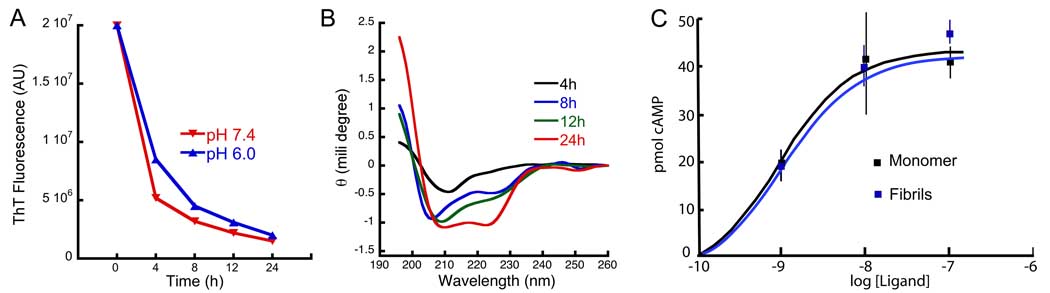
Figure 2.
Release of monomeric, α-helical and functional CRF from its amyloid fibrils. CRF amyloid fibrils were dialyzed against buffer with a 10 kDa cut-off membrane. (A) Time-dependent decrease of Thio T fluorescence inside the membrane at two pH’s as labeled. The decrease of Thio T indicates loss of amyloid fibrils due to dialysis. (B) Time-resolved CD spectroscopy outside the membrane measuring released CRF. The time-dependent increase of the signal indicates release of CRF from the amyloid. The released CRF is likely to be monomeric because of the 10 kDa cut-off of the dialysis membrane. The CD spectrum of the released CRF is of helical structure, which corresponds to the active conformation of CRF. (C) Functional studies of monomeric and amyloid fibrillar sample of CRF by measuring in a hormone concentration-dependent manner the activation of intracellular cyclic AMP in CHO cells stably expressing CRF-R1. Both samples show similar potencies.