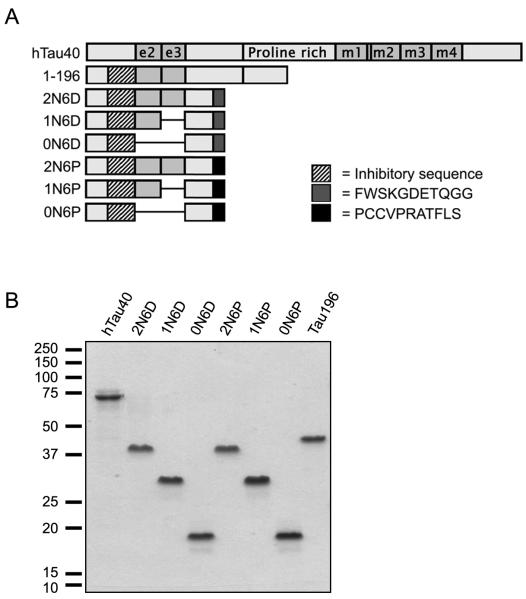
Figure 2.
Schematic of the tau constructs used in this study (A). A tau construct containing a stop codon at Y197 (1-196) has been described elsewhere (5). Constructs containing 0, 1 or 2 alternately spliced N-terminal exons (e2 and e3) were created on the background of the 6P and 6D isoforms. The key indicates the specific N-terminal sequence required to inhibit polymerization of full-length tau (residues 18-42), as well as sequences unique to 6P and 6D isoforms. (B) Depiction of all purified proteins used in this study separated by SDS-PAGE electrophoresis and stained with Coomassie Brilliant Blue R.