Fig. 1.
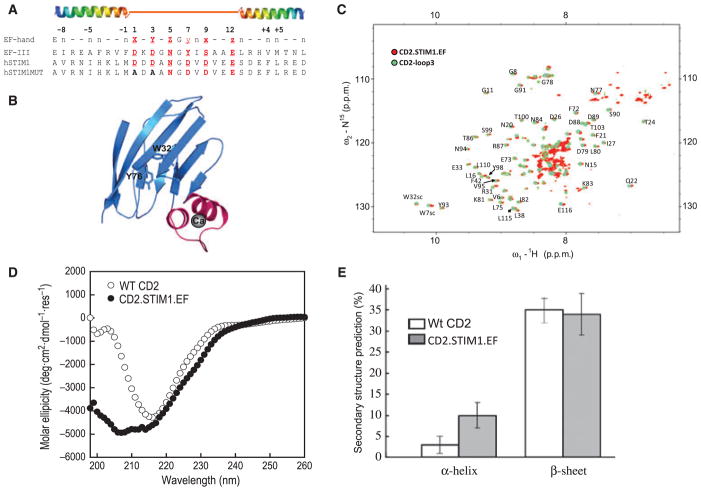
Grafting the helix–loop–helix EF-hand motif into CD2. (A) The sequence alignment results of calmodulin EF-hand III and the canonical EF-hand motif in STIM and its mutant. The sequence from S64 to L96 in STIM1 was grafted into CD2.D1. A mutant containing Asp to Ala substitutions at Ca2+-coordinating loop positions 1 and 3 was introduced to perturb the Ca2+-binding ability of the grafted EF-hand of STIM1. (B) Modelled structure of the engineered protein with the grafted EF-hand Ca2+-binding motif (magenta) from STIM1. W32 and Y76 in the host protein are about 15 Å away from the grafted Ca2+-binding sites. Ca2+ is shown as a dark sphere. (C) Overlay of the (1H, 15N)-HSQC spectrum of CD2.STIM1.EF (red) with that of CD2-loop3 (EF-loop III from calmodulin, cyan) in the absence of Ca2+. (D, E) Far-UV CD spectra of CD2 and CD2.STIM1.EF and the calculated secondary structural contents.