Figure 1.
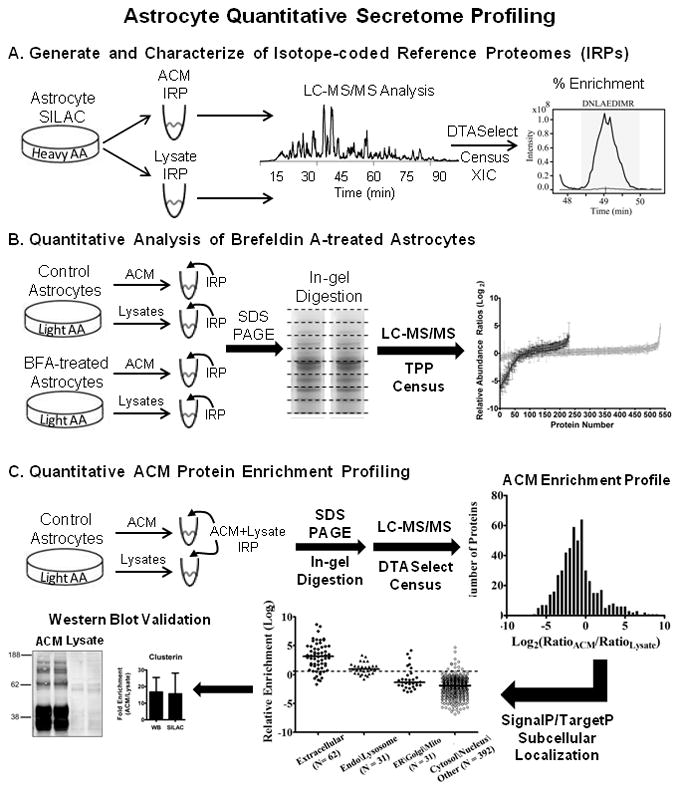
Experimental design and computational analysis of astrocyte protein secretion. (A) Metabolic labeling of proteins by isotope-enriched amino acids (heavy AA) was performed in primary mouse cortical astrocytes cultures by a SILAC-based strategy. After culturing for 20 days in vitro, astrocyte-conditioned media (ACM) and cellular lysates were collected. Protein aliquots were digested in-solution with trypsin and analyzed by LC-MS/MS. Peptide-spectrum matching was performed by SEQUEST/DTASelect, followed by automated reconstruction of extracted ion chromatograms (XIC) and filtering of SILAC peptide/protein ratios by Census quantitative analysis software. Isotope-coded reference proteomes (IRPs) had light-to-heavy (L/H) peptide ratios of ≤ 0.02, corresponding to an enrichment of at least 98 percent. (B) In separate experiments, control and brefeldin A-treated astrocytes were cultured with natural isotope abundance amino acids (light AA). After collection of ACM and cellular lysates, respective IRPs were mixed in known amounts with each sample and analyzed by multidimensional GeLC-MS/MS (SDS-PAGE/In-gel digestion/LC-MS-MS). MS and MS/MS data were analyzed by the TransProteomic Pipeline (TPP) and Census as above to calculate L/H protein ratios. Respective protein ratios calculated for BFA samples were normalized to control protein ratios. (C) A complementary approach to assess the extent of protein secretion was performed by quantifying the relative enrichment of protein in ACM versus cellular lysates. Control ACM and cellular lysates were collected and mixed with a “whole cell” ACM+Lysate IRP. Samples were analyzed by GeLC-MS/MS and the DTASelect/Census quantitative analysis workflow to assemble an ACM protein enrichment profile. Quantified proteins and their respective ratios were evaluated by SignalP/TargetP subcellular localization prediction algorithms. Western blot and LC-MRM-MS/MS analysis (not shown) were also used to independently validate SILAC L/H protein ratios.
