Table I.
Kinetic parameters of eCBL and site-directed mutantsa
| Enzyme | kcat (s−1) |
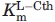 (mM) (mM) |
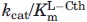 (M−1s−1) (M−1s−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| eCBL | 34.1 ± 0.6 | 0.18 ± 0.01 | (1.9 ± 0.1) × 105 |
| R58A | 9.7 ± 0.3 | 5.1 ± 0.3 | (1.92 ± 0.05) × 103 |
| R58Kb | n.s. | n.s. | 385 ± 1 |
| R59A | 45.8 ± 0.4 | 1.02 ± 0.03 | (4.5 ± 0.1) × 104 |
| R59K | 36.7 ± 0.8 | 1.51 ± 0.09 | (2.4 ± 0.1) × 104 |
| D116A | 41.9 ± 0.7 | 0.67 ± 0.04 | (6.2 ± 0.3) × 104 |
| D116N | 37.9 ± 0.4 | 0.55 ± 0.02 | (6.9 ± 0.2) × 104 |
| W340F | 79 ± 1 | 1.35 ± 0.05 | (5.9 ± 0.2) × 104 |
| R372Ab | n.s. | n.s. | 0.09 ± 0.04 |
| R372K | 8.1 ± 0.8 | 15 ± 2 | 550 ± 20 |
| R372Lb | n.s. | n.s | 0.23 ± 0.03 |
Kinetic parameters reported are for hydrolysis of l-Cth. Reaction conditions: 2 mM DTNB, 0.01–6.4 mM l-Cth and 0.068–6.6 μM wild-type or mutant eCBL, depending on the activity of the enzyme, in assay buffer at 25°C. The data were fit to the Michaelis-Menten equation to obtain kcat and 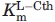 and equation 1 to obtain
and equation 1 to obtain 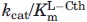 .
.
n.s. indicates that 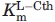 exceeds the solubility limit of the l-Cth, such that
exceeds the solubility limit of the l-Cth, such that 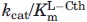 was determined via linear regression.
was determined via linear regression.
