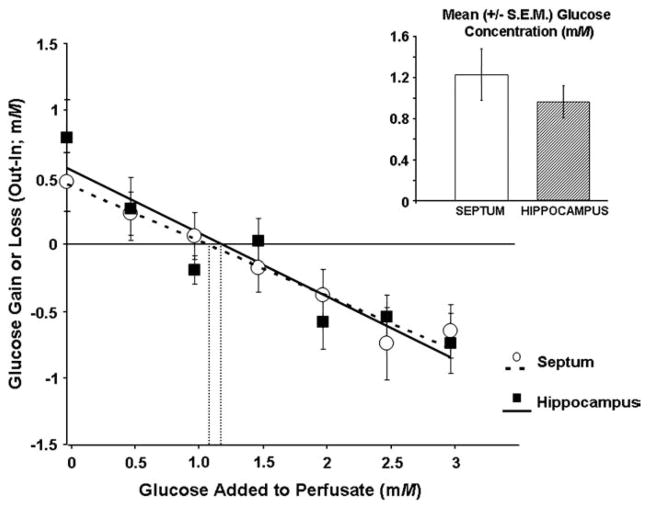
Fig. 2.
Glucose gain or loss to the brain as a function of perfusate concentration (0–3 mM) in the septum or hippocampus of rats using dual-probe microdialysis procedures. The point of zero net flux is the estimated extracellular fluid concentration of glucose. The solid (hippocampus) and dashed (septum) lines are the line of best fit for the point of zero net flux determination. The insert shows the mean (±S.E.M.) estimated glucose concentrations based on the individual regression analyses of each rat. The extracellular fluid glucose concentration in the septum (1.22±.25 mM) and the hippocampus (0.96±.16 mM) do not differ significantly (P>.05).