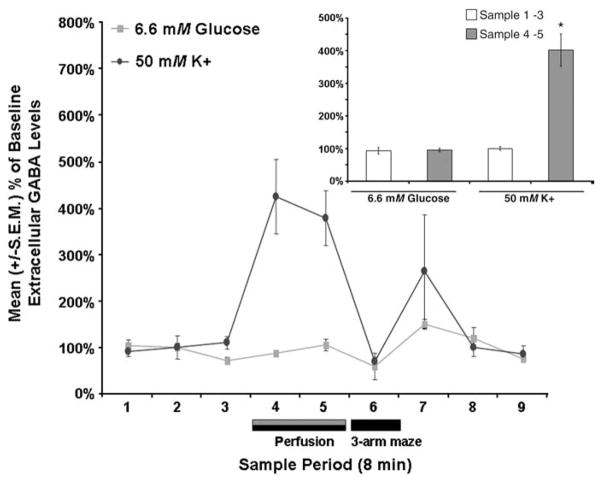
Fig. 7.
Septal perfusions of 6.6 mM glucose did not significantly affect mean (±S.E.M.) extracellular fluid GABA levels (P>.05) whereas septal perfusions of 50 mM potassium did (P<.05). Inset shows the pooled mean (±S.E.M.) extracellular fluid GABA values for the baseline samples (i.e., samples 1–3) and the extracellular fluid GABA values for the two post-baseline samples in which glucose or potassium were elevated (i.e., samples 4–5). Septal perfusion of glucose (6.6 mM) did not significantly affect mean septal extracellular fluid GABA levels (P>.05 vs. baseline). The mean septal extracellular fluid GABA levels in the samples in which potassium was elevated were significantly higher than the extracellular fluid GABA values of the baseline samples (P<.05).