Abstract
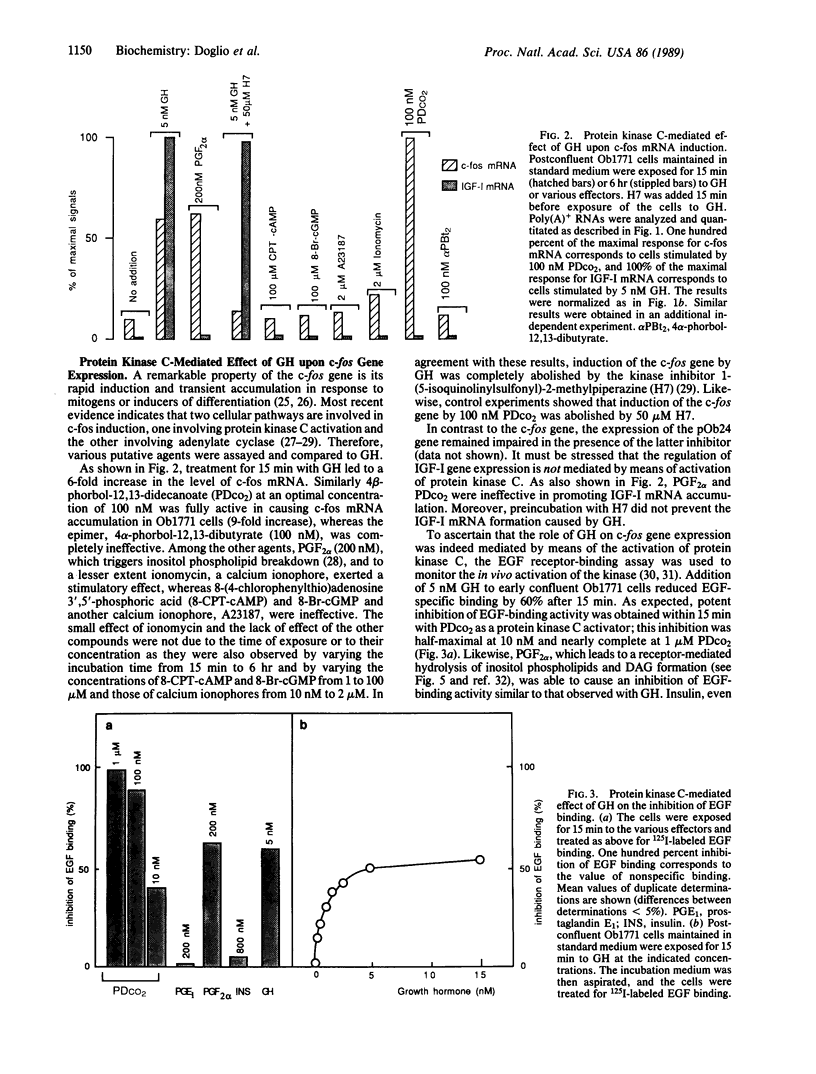
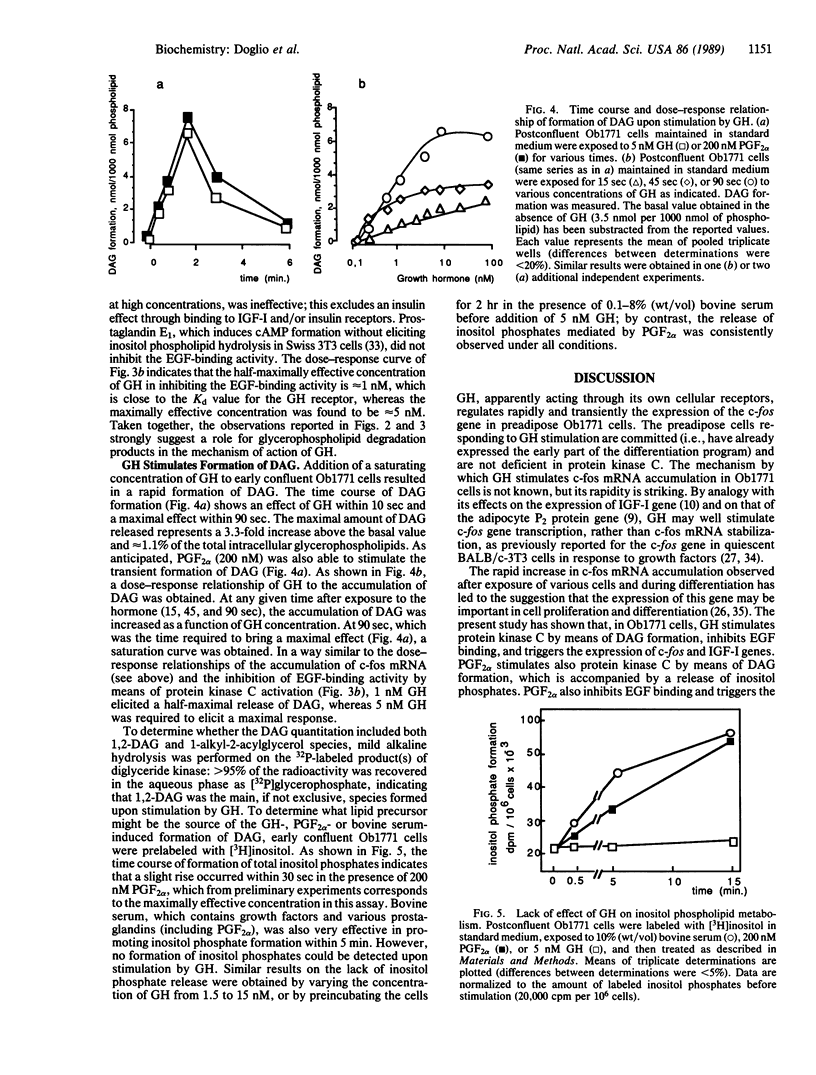
Growth hormone (GH) is required for the terminal differentiation of preadipose Ob1771 cells that have entered the differentiation program as evidenced by the expression of early marker genes (pOb24 and lipoprotein lipase). Induction of c-fos mRNA within 15 min and induction of insulin-like growth factor I mRNA within a few hours take place in response to GH. The role of GH is mediated, at least in part, by means of the activation of protein kinase C, as shown by the inhibition of epidermal growth factor binding and by the expression of the c-fos gene, and is thus analogous to the action of prostaglandin F2 alpha and 4 beta-phorbol-12,13-didecanoate in this respect. However, in contrast to that of the c-fos gene, the regulation of insulin-like growth factor I gene expression by GH is not mediated by means of the activation of protein kinase C, and, in line with this, prostaglandin F2 alpha and 4 beta-phorbol-12,13-didecanoate were ineffective. GH and prostaglandin F2 alpha were able to stimulate the formation of diacyglycerol within a few seconds, but GH did not elicit an accumulation of inositol phosphates, in contrast to that generated by prostaglandin F2 alpha. We conclude that the transduction signal of GH action in c-fos mRNA induction is the formation of diacylglycerol and that the mechanism whereby GH can activate protein kinase C is associated with a phospholipase C-mediated hydrolysis of glycerophospholipids other than inositol phospholipids.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AMES B. N., DUBIN D. T. The role of polyamines in the neutralization of bacteriophage deoxyribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1960 Mar;235:769–775. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amri E. Z., Dani C., Doglio A., Etienne J., Grimaldi P., Ailhaud G. Adipose cell differentiation: evidence for a two-step process in the polyamine-dependent Ob1754 clonal line. Biochem J. 1986 Aug 15;238(1):115–122. doi: 10.1042/bj2380115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amri E. Z., Dani C., Doglio A., Grimaldi P., Ailhaud G. Coupling of growth arrest and expression of early markers during adipose conversion of preadipocyte cell lines. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Jun 13;137(2):903–910. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)91165-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell R. M. Protein kinase C activation by diacylglycerol second messengers. Cell. 1986 Jun 6;45(5):631–632. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90774-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Irvine R. F. Inositol trisphosphate, a novel second messenger in cellular signal transduction. Nature. 1984 Nov 22;312(5992):315–321. doi: 10.1038/312315a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Besterman J. M., Duronio V., Cuatrecasas P. Rapid formation of diacylglycerol from phosphatidylcholine: a pathway for generation of a second messenger. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):6785–6789. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.6785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop W. R., Bell R. M. Functions of diacylglycerol in glycerolipid metabolism, signal transduction and cellular transformation. Oncogene Res. 1988 Feb;2(3):205–218. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Björgell P., Rosberg S., Isaksson O., Belfrage P. The antilipolytic, insulin-like effect of growth hormone is caused by a net decrease of hormone-sensitive lipase phosphorylation. Endocrinology. 1984 Sep;115(3):1151–1156. doi: 10.1210/endo-115-3-1151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bravo R., Neuberg M., Burckhardt J., Almendral J., Wallich R., Müller R. Involvement of common and cell type-specific pathways in c-fos gene control: stable induction of cAMP in macrophages. Cell. 1987 Jan 30;48(2):251–260. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90428-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown K. D., Blay J., Irvine R. F., Heslop J. P., Berridge M. J. Reduction of epidermal growth factor receptor affinity by heterologous ligands: evidence for a mechanism involving the breakdown of phosphoinositides and the activation of protein kinase C. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Aug 30;123(1):377–384. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)90424-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cameron C. M., Kostyo J. L., Adamafio N. A., Brostedt P., Roos P., Skottner A., Forsman A., Fryklund L., Skoog B. The acute effects of growth hormone on amino acid transport and protein synthesis are due to its insulin-like action. Endocrinology. 1988 Feb;122(2):471–474. doi: 10.1210/endo-122-2-471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Distel R. J., Ro H. S., Rosen B. S., Groves D. L., Spiegelman B. M. Nucleoprotein complexes that regulate gene expression in adipocyte differentiation: direct participation of c-fos. Cell. 1987 Jun 19;49(6):835–844. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90621-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doglio A., Dani C., Fredrikson G., Grimaldi P., Ailhaud G. Acute regulation of insulin-like growth factor-I gene expression by growth hormone during adipose cell differentiation. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 20;6(13):4011–4016. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02744.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doglio A., Dani C., Grimaldi P., Ailhaud G. Growth hormone regulation of the expression of differentiation-dependent genes in preadipocyte Ob1771 cells. Biochem J. 1986 Aug 15;238(1):123–129. doi: 10.1042/bj2380123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donnér J., Eriksson H., Belfrage P. The acute GH action in rat adipocytes is associated with enhanced phosphorylation of a 46 kDa plasma membrane protein enriched by GH-Sepharose. FEBS Lett. 1986 Nov 24;208(2):269–272. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)81030-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Froesch E. R., Schmid C., Schwander J., Zapf J. Actions of insulin-like growth factors. Annu Rev Physiol. 1985;47:443–467. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.47.030185.002303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg M. E., Ziff E. B. Stimulation of 3T3 cells induces transcription of the c-fos proto-oncogene. Nature. 1984 Oct 4;311(5985):433–438. doi: 10.1038/311433a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimaldi P., Czerucka D., Rassoulzadegan M., Cuzin F., Ailhaud G. ob17 cells transformed by the middle-T-only gene of polyoma virus differentiate in vitro and in vivo into adipose cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(17):5440–5444. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.17.5440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hakeda Y., Hotta T., Kurihara N., Ikeda E., Maeda N., Yagyu Y., Kumegawa M. Prostaglandin E1 and F2 alpha stimulate differentiation and proliferation, respectively, of clonal osteoblastic MC3T3-E1 cells by different second messengers in vitro. Endocrinology. 1987 Dec;121(6):1966–1974. doi: 10.1210/endo-121-6-1966. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollenberg C. H., Vost A. Regulation of DNA synthesis in fat cells and stromal elements from rat adipose tissue. J Clin Invest. 1969 Nov;47(11):2485–2498. doi: 10.1172/JCI105930. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isaksson O. G., Edén S., Jansson J. O. Mode of action of pituitary growth hormone on target cells. Annu Rev Physiol. 1985;47:483–499. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.47.030185.002411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knittle J. L. Obesity in childhood: a problem in adipose tissue cellular development. J Pediatr. 1972 Dec;81(6):1048–1059. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(72)80231-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacal J. C., Moscat J., Aaronson S. A. Novel source of 1,2-diacylglycerol elevated in cells transformed by Ha-ras oncogene. Nature. 1987 Nov 19;330(6145):269–272. doi: 10.1038/330269a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund P. K., Moats-Staats B. M., Hynes M. A., Simmons J. G., Jansen M., D'Ercole A. J., Van Wyk J. J. Somatomedin-C/insulin-like growth factor-I and insulin-like growth factor-II mRNAs in rat fetal and adult tissues. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 5;261(31):14539–14544. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnaldo I., L'Allemain G., Chambard J. C., Moenner M., Barritault D., Pouysségur J. The mitogenic signaling pathway of fibroblast growth factor is not mediated through polyphosphoinositide hydrolysis and protein kinase C activation in hamster fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1986 Dec 25;261(36):16916–16922. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morikawa M., Nixon T., Green H. Growth hormone and the adipose conversion of 3T3 cells. Cell. 1982 Jul;29(3):783–789. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90440-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preiss J. E., Loomis C. R., Bell R. M., Niedel J. E. Quantitative measurement of sn-1,2-diacylglycerols. Methods Enzymol. 1987;141:294–300. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)41077-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rider L. G., Dougherty R. W., Niedel J. E. Phorbol diesters and dioctanoylglycerol stimulate accumulation of both diacylglycerols and alkylacylglycerols in human neutrophils. J Immunol. 1988 Jan 1;140(1):200–207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saltiel A. R., Sherline P., Fox J. A. Insulin-stimulated diacylglycerol production results from the hydrolysis of a novel phosphatidylinositol glycan. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 25;262(3):1116–1121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlechter N. L., Russell S. M., Spencer E. M., Nicoll C. S. Evidence suggesting that the direct growth-promoting effect of growth hormone on cartilage in vivo is mediated by local production of somatomedin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(20):7932–7934. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.20.7932. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seuwen K., Lagarde A., Pouysségur J. Deregulation of hamster fibroblast proliferation by mutated ras oncogenes is not mediated by constitutive activation of phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C. EMBO J. 1988 Jan;7(1):161–168. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02796.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smal J., De Meyts P. Role of kinase C in the insulin-like effects of human growth hormone in rat adipocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Sep 30;147(3):1232–1240. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(87)80202-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stumpo D. J., Blackshear P. J. Insulin and growth factor effects on c-fos expression in normal and protein kinase C-deficient 3T3-L1 fibroblasts and adipocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9453–9457. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stumpo D. J., Stewart T. N., Gilman M. Z., Blackshear P. J. Identification of c-fos sequences involved in induction by insulin and phorbol esters. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 5;263(4):1611–1614. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman R. Transient accumulation of c-fos RNA following serum stimulation requires a conserved 5' element and c-fos 3' sequences. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):889–902. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90285-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuda T., Hamamori Y., Yamashita T., Fukumoto Y., Takai Y. Involvement of three intracellular messenger systems, protein kinase C, calcium ion and cyclic AMP, in the regulation of c-fos gene expression in Swiss 3T3 cells. FEBS Lett. 1986 Nov 10;208(1):39–42. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)81527-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verma I. M., Sassone-Corsi P. Proto-oncogene fos: complex but versatile regulation. Cell. 1987 Nov 20;51(4):513–514. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90115-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verma S. S., Gupta R. K., Kishore N., Sen Gupta J. A simple relationship between maximal aerobic power and body weight in Indian adolescent boys. Indian J Med Sci. 1986 Apr;40(4):93–96. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamashita T., Takai Y. Inhibition of prostaglandin E1-induced elevation of cytoplasmic free calcium ion by protein kinase C-activating phorbol esters and diacylglycerol in Swiss 3T3 fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 25;262(12):5536–5539. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]