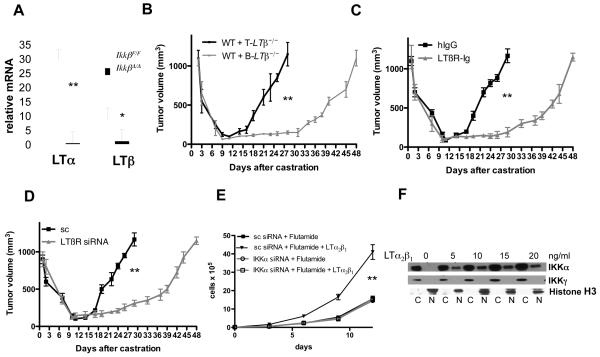
Figure 4. IKKβ-dependent lymphotoxin production by tumor-infiltrating B cells stimulates IKKα-dependent androgen-free survival.
A. RNA from splenic B cells of IkkβF/F and IkkβΔ/Δ mice was analyzed for LTα and LTβ expression as above. Results are averages ± s.d. (n=3). B. Lethally irradiated FVB males were reconstituted with BM from B-Ltβ−/− or T-Ltβ−/− mice (n=6 per group). After 8 weeks, myc-CaP tumors were established, mice were castrated and tumor volume was measured as above. Results are averages ± s.e.m.. C. FVB mice (n=6 each group) bearing myc-CaP tumors were castrated and given hIgG or LTβR-Ig (100 μg) every 5 days, starting 4 days before castration. Tumor volume was measured as above. Results are averages ± s.e.m.. D. Tumors were established using myc-CaP cells transduced with lentiviruses expressing scrambled (sc) siRNA or LTβ-specific siRNA. Mice were castrated and tumor volume was measured. Results are averages ± s.e.m. (n=10). E. Myc-CaP cells (previously infected with lentiviruses expressing scrambled or IKKα siRNAs) were plated at 40% confluency. After 6 hrs, the cells were cultured with or without flutamide (10 μM) in the absence or presence of LTα2β1, and cell number was determined. F. Myc-CaP cells were plated at 60% confluency. After 12 hrs, cells were stimulated for 1 hr with LTα2β1, collected, divided into cytosolic (C) and nuclear (N) fractions and IKKα and histone H3 distribution was determined. In A, B, C, D and E, P values were determined and are indicated as above.