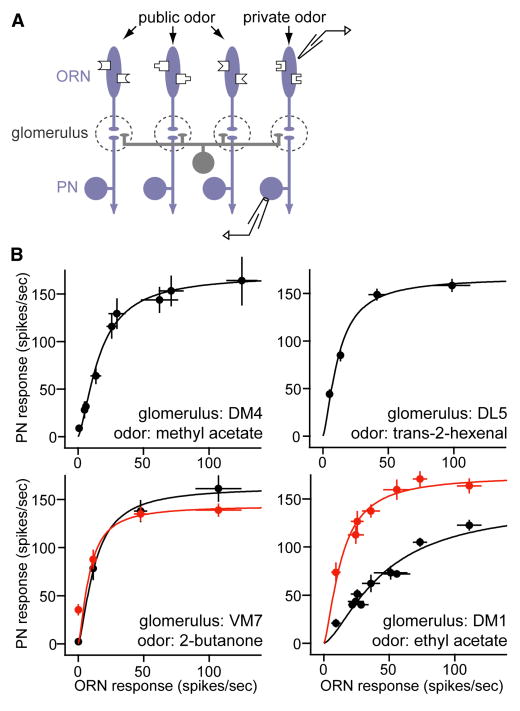
Figure 1. A generalized intra-glomerular transformation.
A. Experimental design. Varying the concentration of a private odor stimulus activates one ORN type to varying degrees. Recordings are performed from both these ORNs and their cognate PNs. In this figure, we use only private odors. In the experiments that follow, we will blend in a public odor that activates other ORNs (but not the cognate ORNs of the PNs we are recording from). This allows us to manipulate direct and lateral input independently.
B. Intra-glomerular input-output functions for four glomeruli. Within a graph, each point is a different concentration of the same private odor. GABA receptor antagonists (5 μM picrotoxin +10 μM CGP54626) increase the gain in DM1 but not VM7 (red). All values are means of 6 -12 recordings, ± SEM. Curves are best fits to Equation (1). Concentrations are: methyl acetate 0, 10-11, 10-10, 10-9, 3×l0-8, 7×l0-8, 10-7, 10-6, 10-5; trans-2-hexenal 10-9, 10-8, 10-7, 5×l0-7; 2-butanone 10-7, 10-6, 10-5, 10-4; ethyl acetate 0, 10-14, 10-13, 10-12, 10-11, 10-9, 10-8, 10-7, 10-6.