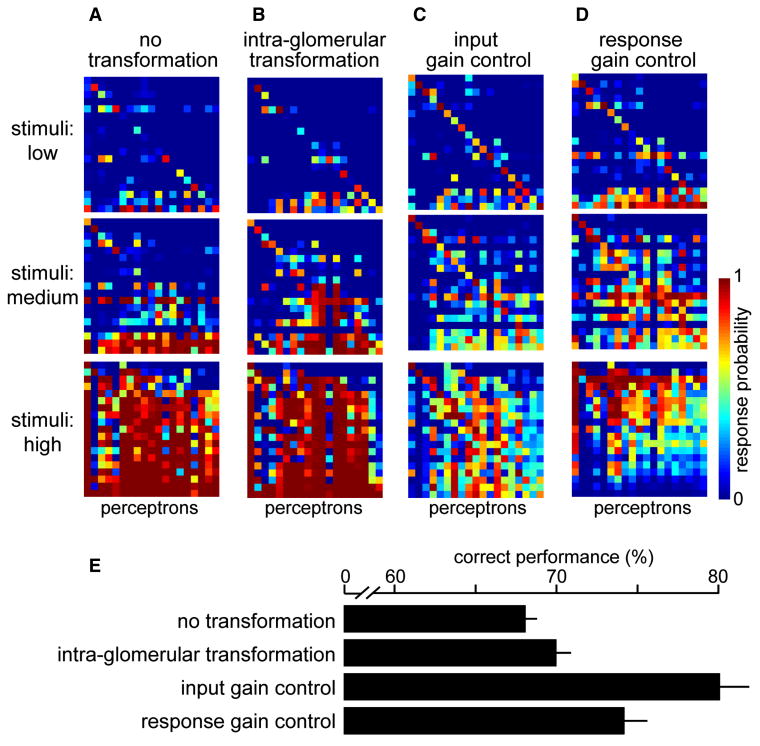
Figure 7. Input gain control promotes concentration-invariant discrimination.
A-D. Confusion matrices show the performance of 19 perceptrons trained to respond to a chemical stimulus regardless of concentration. Perceptron 1 is trained to target odor 1 at low, medium, and high concentrations; perceptron 2 is trained to target odor 2 at low, medium, and high concentrations, etc.
E. Mean performance for each set of perceptrons, averaged across 500 independent networks, ± SD.