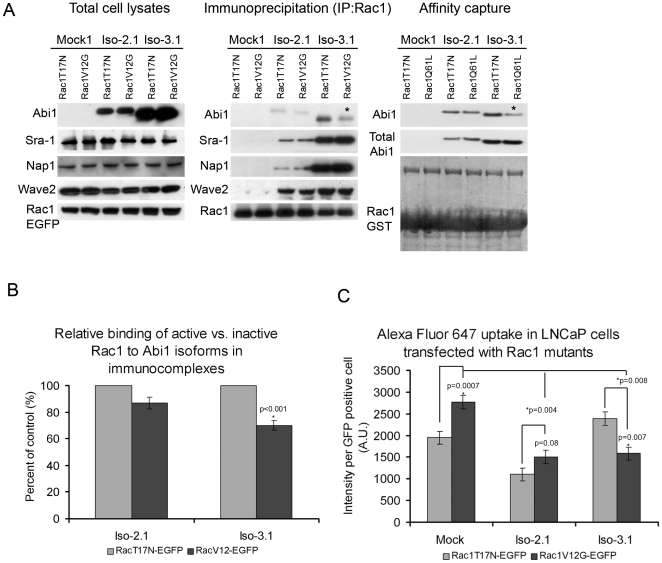
Figure 4. Active Rac1 interacts differentially with Abi1 isoforms.
A. Comparison of Rac1 mutant interactions with Abi1 isoforms. Constitutively active Rac1-V12G (GFP-Rac1-V12G) or dominant negative Rac1-T17N (GFP-Rac1-T17N), were transfected separately and analyzed in Abi1 isoform expressing LNCaP cell lines as described in Materials and Methods. Membranes were blotted with anti-HA, anti-Sra-1, anti-Nap1 or anti-Wave2 antibodies to demonstrate the level of co-immunoprecipitated Wave 2 complex components; or with GFP antibody (GFP-Rac1-V12G, or GFP-Rac1-T17N) to demonstrate the level of immunoprecipitated Rac1. (Right panel) Immunoprecipitation results were further confirmed in affinity capture analyses where cell lysates from Iso-2.1 or Iso-3.1 expressing cell lines were subjected to pull down with either GST tagged Rac1 T17N (inactive) or Q61L (active) mutants used as baits. B. Quantification of Rac1 binding to Abi1 isoforms in immunoprecipitation experiments. Relative binding of active vs. inactive Rac1 to Abi1 isoforms was evaluated from proteins band intensities in three independent immunoprecipitation experiments. C. Alexa Fluor 647 uptake in LNCaP cells transfected with active Rac1 shows opposite effects in Iso-2.1 compared to Iso-3.1 cell lines. Measurements were performed in triplicate, n = 3, error bars ± s.e.m.