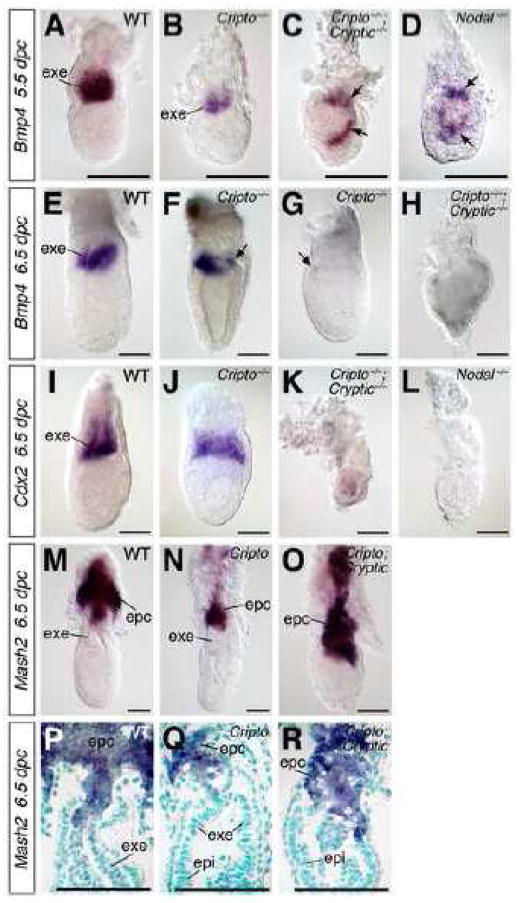
Figure 4.
Expression of extraembryonic ectoderm (ExE) and ectoplacental cone markers in wild-type, Cripto, and Cripto; Cryptic mutants. (A–D) Bmp4 is expressed at 5.5 dpc in the ExE of wild-type (A), but is found only in the most distal part of the ExE in Cripto−/− mutants (B). Expression of Bmp4 is severely mislocalized in the presumptive epiblast (arrows) of Cripto−/−; Cryptic−/− double mutants (C) as well as Nodal−/− mutants (D). (E–H) At 6.5 dpc, Bmp4 is expressed in the distal ExE in wild-type (E), but is either reduced or nearly absent in Cripto−/− single mutants (arrows in F, G), and is lost entirely in Cripto−/−; Cryptic−/− double mutants (H). (I–L) Expression of Cdx2 at 6.5 dpc in the ExE in wild-type (I) is nearly normal in Cripto−/− mutants (J), but is absent in both Cripto−/−; Cryptic−/− double mutants (K) and Nodal−/− mutants (L). (M–O) Expression of Mash2 in the ectoplacental cone of wild-type (M), putative Cripto mutant (N) and putative Cripto; Cryptic double mutant (O) embryos, showing an expanded domain of Mash2 expression in the double mutant. (P–R) Longitudinal sections of the embryos shown in M–O, respectively; nuclei are counterstained with methyl green. In M–R, embryo genotypes were deduced from phenotypes, and the Cripto; Cryptic double mutant may correspond to either Cripto−/−; Cryptic−/− and Cripto−/−; Cryptic+/− genotypes. Scale bars correspond to 100 microns. Abbreviations: epc, ectoplacental cone; epi, epiblast; exe, extraembryonic ectoderm.