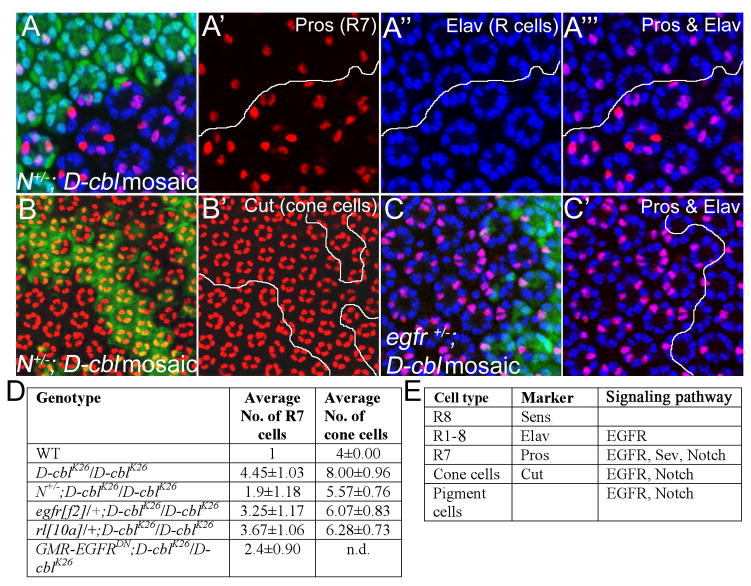
Figure 2. Partial rescue of R7 and cone cell defects in egfr+/− and N+/− background.
Analysis of R7, photoreceptors (R cells) (A-A‴) and cone cells (B,B′) in D-cblK26 clones in heterozygous Notch (N) background by Pros/Elav (red/blue) double labelings (A-A‴) and Cut (red) labelings (B,B′) in 42 hrs APF pupal eye imaginal discs. Mutant clones are outlined by white lines in A′-A‴ and B′. Compared to D-cblK26 clones alone (Fig. 7A,B), R7 and cone cells are significantly reduced in N/+;D-cbl mutant ommatidia (see quantification in D). Genotype: ey-Flp/Df(1)N8; D-cblK26 FRT80/P[ubi-GFP] FRT80.
(C,C′) Anti-Pros (red) and anti-Elav (blue) double labeling of D-cblK26 mosaics heterozygous for egfr in 42 hours APF eye disc. Mutant clones are outlined by white lines in C′. Genotype: ey-Flp; egfrf2/+; D-cblK26 FRT80/P[ubi-GFP] FRT80.
(D) Summary of the total number of R7 and cone cells in 42 hrs APF pupal eye imaginal discs of the indicated genotypes as determined by Anti-Pros and Elav staining. A total of 35 ommatidia were counted for each genotype.
(E) List of cell type-specific markers and the signaling pathways involved in specification of the cell types listed.