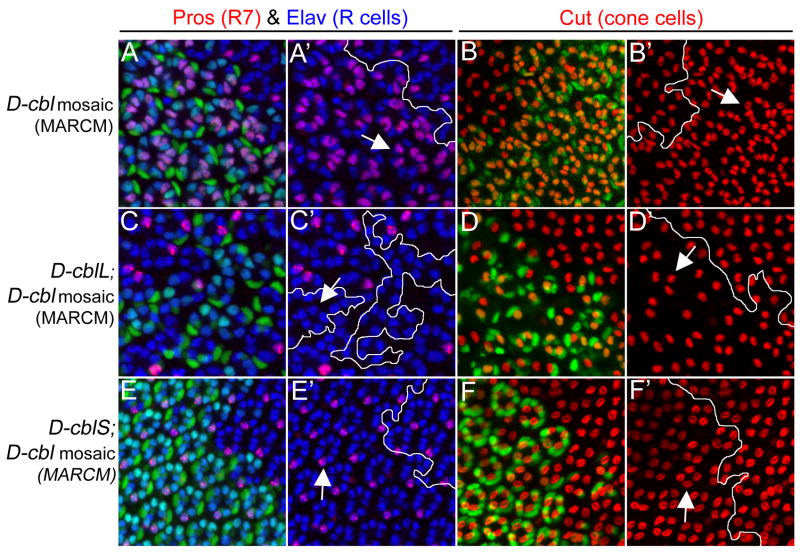
Figure 7. Distinct rescue of the D-cbl over-recruitment phenotype by expression of the D-cbl isoforms.
Shown are pupal (42h APF) eye discs labeled with anti-Pros/Elav antibodies (red/blue) for R7/photoreceptor (R) cells and anti-Cut antibody (red) for cone cells. D-cbl mutant clones are positively labeled by GFP due to the MARCM technique (outlined by white lines) and express either no transgene (A,A′,B,B′), D-cblL (C,C′,D,D′) or D-cblS (E,E′F,F′). GFP-negative cells are non-mutant (wild-type or heterozygous) and do not express any transgene. Arrows point to representative examples of the phenotypes in the mutant clones as explained in the text. The null allele D-cblK26, and the transgenes UAS-D-cblL (line A18) and UAS-D-cblS (line A1) transgenes were used.
Genotypes:
(A,B) hs-Flp actin-Gal4 UAS-GFP; D-cblK26 FRT80/tub-Gal80 FRT80;
(C,D) hs-Flp actin-Gal4 UAS-GFP; UAS-D-cblL/+; D-cblK26 FRT80/tub-Gal80 FRT80;
(E,F) hs-Flp actin-Gal4 UAS-GFP; UAS-D-cblS/+; D-cblK26 FRT80/tub-Gal80 FRT80.