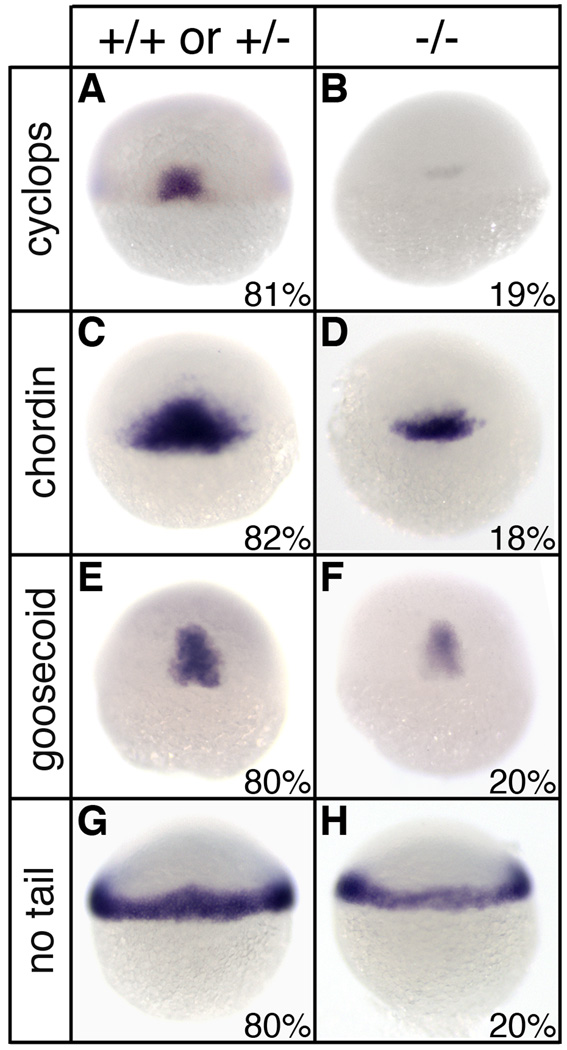
Fig. 6.
Reduced mesodermal gene expression in sym1 mutants. Heterozygous sym1 adults were crossed and progeny were examined for mesodermal gene expression by in situ hybridization at shield stage (6hpf). For cyclops (A,B), chordin (C,D), goosecoid (E,F), and no tail (G,H), two phenotypic classes were observed: wild-type (A,C,E,G) and reduced gene expression (B,D,F,H). For each mesodermal gene analyzed, distribution of progeny into the two classes was ~80% for the wild-type class and ~20% for the reduced class (exact distribution for each gene is indicated in lower right of each panel). Representative embryos were selected for genotyping analysis following in situ hybridization and this indicated that the wild-type phenotypic class consisted of both genotypically wild-type (+/+) and sym1 heterozygotes (+/−), while the reduced gene expression class consisted only of sym1 homozygotes (−/−). Dorsal views are shown.