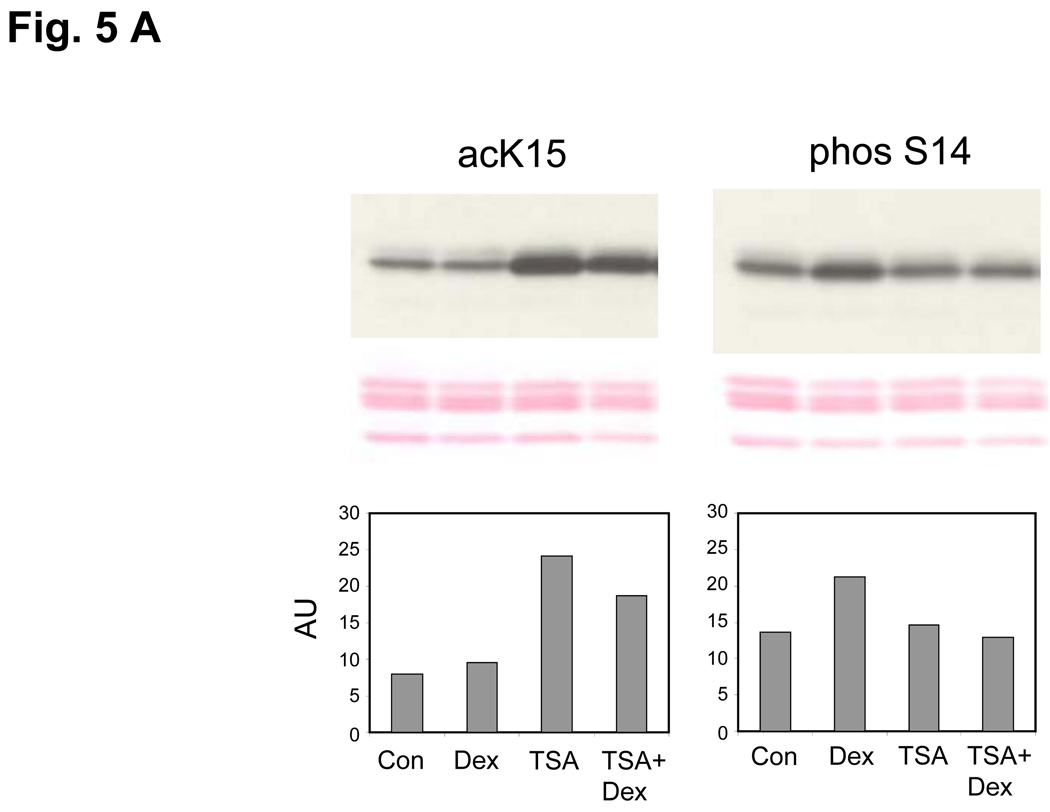
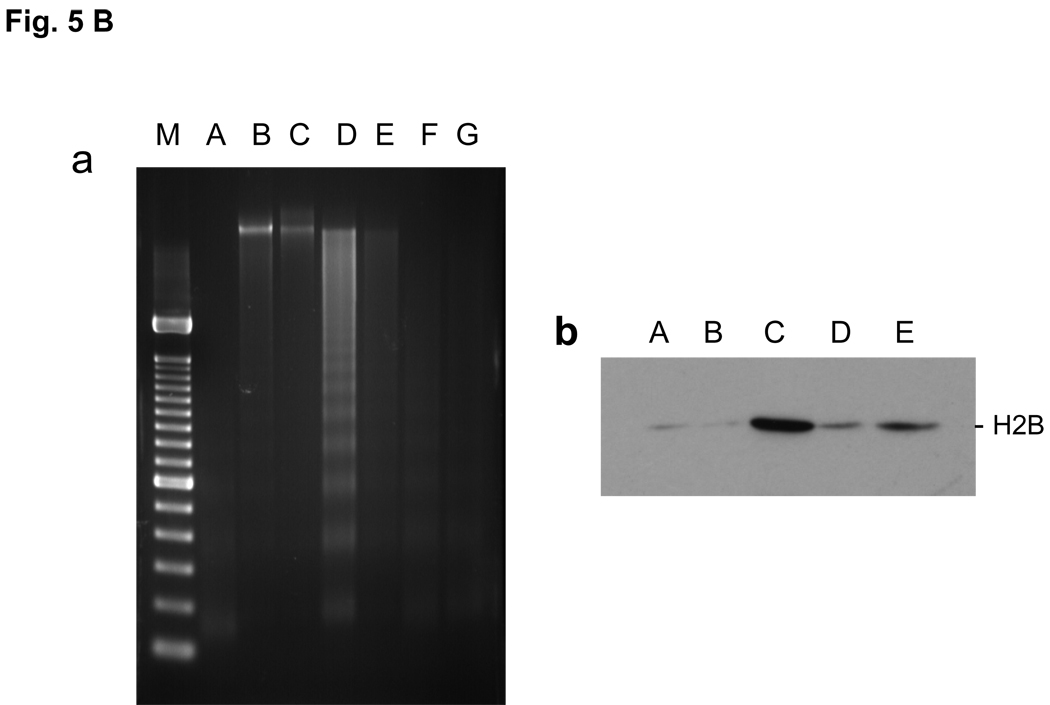
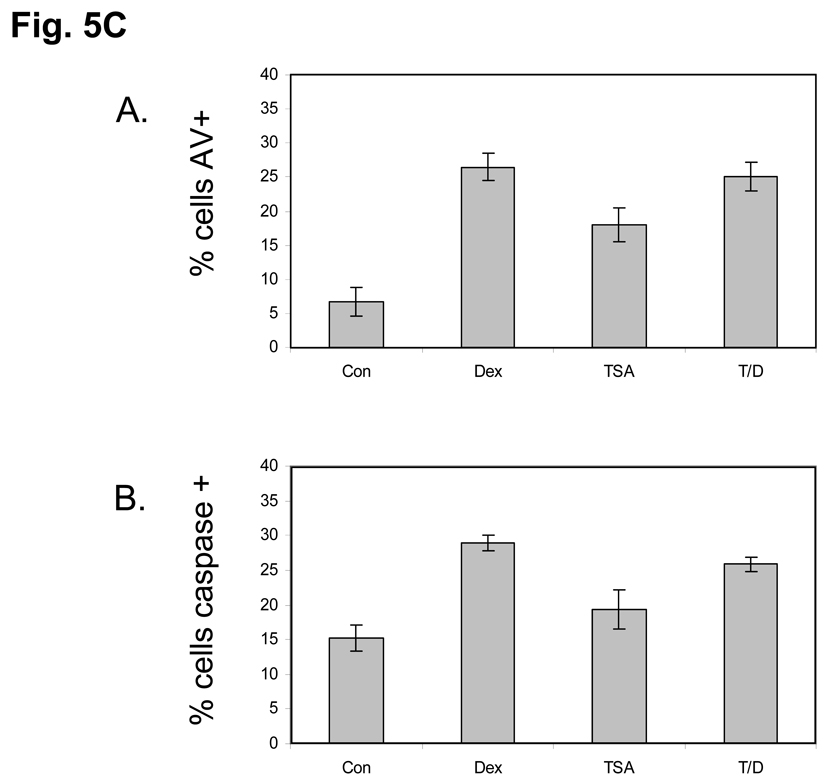
FIG. 5. Effect of TSA on histone K15 acetylation, S14 phosphorylation and DNA degradation.
(A) Enhancement of K15 and suppression of S14 phosphorylation by a HDAC inhibitor (TSA). Dex, Thymocytes were treated with 1 µM dexamethasone; TSA, 1 µM TSA for 3 h, TSA+Dex, pretreated with 1 µM TSA for 1 h and treated with 1 µM Dexamethasone for 3 h. Histones were extracted and western blotted against acK15 (left) and phosS14 (right). Histones obtained from whole chromatin show a smaller decrease of acK15 in the dexamethasone treated thymocytes as compared to Fig. 4B, which was obtained from soluble chromatin from apoptotic cells. The data shown represents three experiments.
(B) TSA prevents Dex induced DNA degradation and histone release in soluble chromatin
a. Prevention of DNA degradation. Thymocytes were incubated at 37°C for 4 hrs. Nuclei were isolated. The nuclei were treated with lysis buffer and the soluble chromatin was treated with RNase and proteinase K and run on 1.8% agarose gel electrophoresis. M, DNA size marker same as shown in Fig. 1C, A, Fresh thymocytes. B, Control thymocytes incubated without chemicals. C, thymocytes with 10 nM Dex. D, 100 nM Dex. E, 1 µM TSA. F, TSA with 10 nM Dex. G, TSA with 100 nM Dex.
b. Prevention of histone release. The soluble chromatin was obtained from thymocytes as described above (a). The soluble chromatin was run on SDS-PAGE gel then analyzed by western blot against anti-H2B. A Fresh thymocytes, B, Control thymocytes incubated without chemicals. C, 100 nM Dex, D, 1 µM TSA, E, TSA with 100 nM Dex.
(C) TSA does not prevent apoptosis in Dex treated Thymocytes. Isolated rat thymocytes were treated with Dex 1µM, TSA 1 µM, TSA+Dex or left untreated for 6 hours. Annexin-V binding and caspase 3-like activity was analyzed by flow cytometry. Dead cells were not used in the analysis. A. Dex, TSA alone and TSA plus Dex treatment all caused an increase in the percentage of Annexin-positive cells. B. Dex, TSA alone and TSA plus Dex treatment all caused an increase in the percentage of cells with caspase 3-like activity.