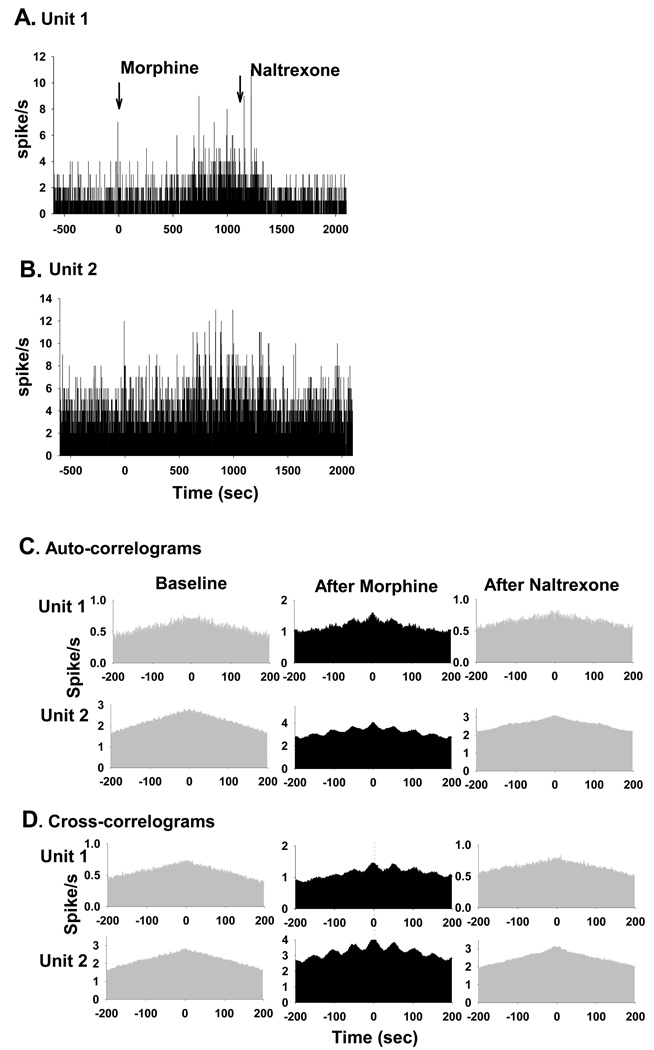
Fig. 2.
Effects of morphine on temporal relationship among PGi neurons’ activities. (A) and (B) Histograms of spontaneous firing rates of 2 simultaneously recorded PGi neurons (Unit 1 and Unit 2) before and after morphine and naltrexone injections. Morphine was injected at time 0 (26 nmol, i.c.v.). Naltrexone was injected 20 min after morphine administration. (C) Auto-correlograms of the two PGi neurons before and after morphine and naltrexone injections. Note the large satellite peaks after morphine and lack of satellite peaks after naltrexone. (D) Cross-correlograms of the two neurons before and after morphine and naltrexone injections. Note the large central peaks after morphine and lack of central peaks after naltrexone.