Fig. 3.
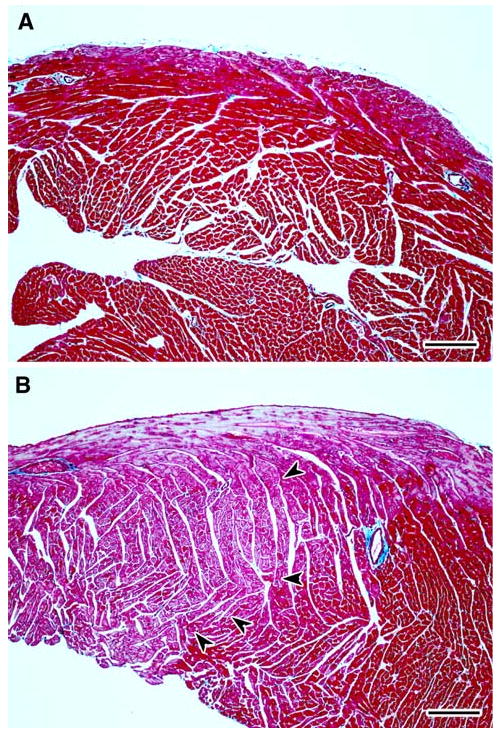
a–b Representative light photomicrographs of right ventricular free wall from cardiac tissue sections stained with Masson's trichrome from female CD-1 mice necropsied at 13 week of age following transplacental exposure to vehicle (a) or AZT/3TC (b). a shows uniform normochromic (dark red) trichrome staining in the right ventricle of a heart from a control mouse, while b has areas of apparent normochromic staining juxtaposed to areas of uniform pallor (orchid color) in the right ventricle of a heart from a mouse exposed in utero to AZT/3TC. In b, a line of demarcation between hypochromic areas (left) and normochromic areas (right) of cardiomyocytes is indicated by arrowheads. The light blue staining pattern at the top of the right ventricle in b is a result of the presence of subepicardial Purkinje fibers. Bar represents 150 μm
