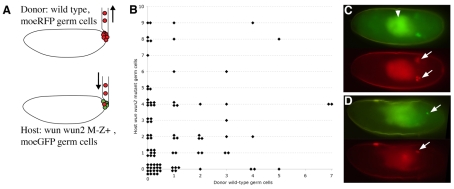
Fig. 5.
Transplantation of wild-type germ cells does not rescue wun wun2-null germ cell survival. (A) Transplantation scheme. Germ cells from stage-5 nos>moeRFP embryos (donor) were injected into the posterior pole of stage-5 embryos laid by wun wun2 germ line clone females (wun wun2 M–Z+) carrying nosGAL4VP16 mated to UAS moeGFP males (host). (B) Scattergram showing the number of host mutant germ cells in soma or gonad versus the number of donor wild-type germ cells in soma or gonad. (C,D) Fluorescent images of living embryos, anterior to the left, showing host moeGFP germ cells (green) and transplanted moeRFP germ cells (red). (C) Stage-15 wild-type host embryo. Transplanted germ cells are able to survive and migrate to the gonads (arrows). The gut autofluorescence is marked with an arrowhead. (D) Stage-14 wun wun2 M–Z+ host embryo showing a single surviving host germ cell (upper arrow) and two transplanted germ cells (lower arrow).