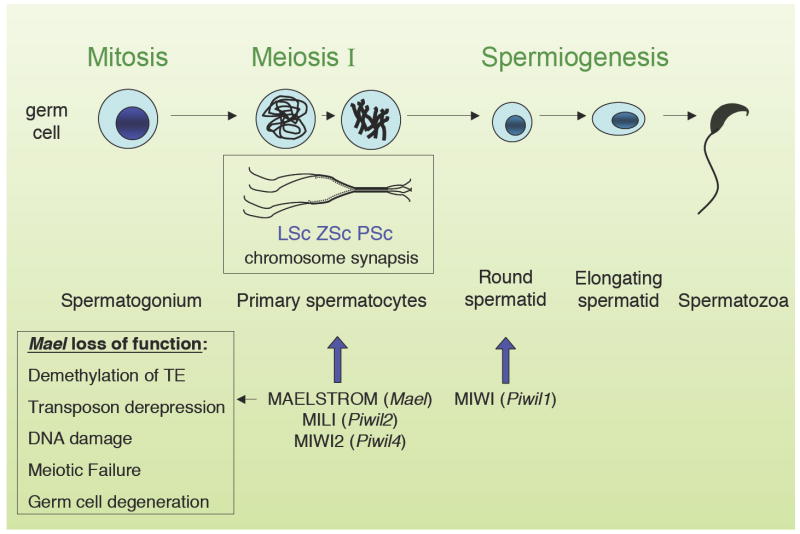
Figure 1.
The three phases of spermatogenesis in mice: mitosis, meiosis, and spermiogenesis. During mitosis, stem cells divide to generate primary spermatocytes. These proceed through meiosis I and II to generate haploid round spermatids. Meiotic prophase I is further divided into several stages: In leptotene spermatocytes (LSc), chromosomes condense and sister chromatids pair. In zygotene spermatocytes (ZSc), synaptonemal complex components are organized for pairing of homologs. Crossover occurs in pachytene spermatocytes (PSc), resulting in the exchange of genetic information. Homologous chromosomes separate in diplotene and resolve in diakinesis. During spermiogenesis, after the second meiotic division, round spermatids mature to elongated forms and spermatozoa. Meiotic arrest points are indicated for mouse Maelstrom and Piwi family mutants.