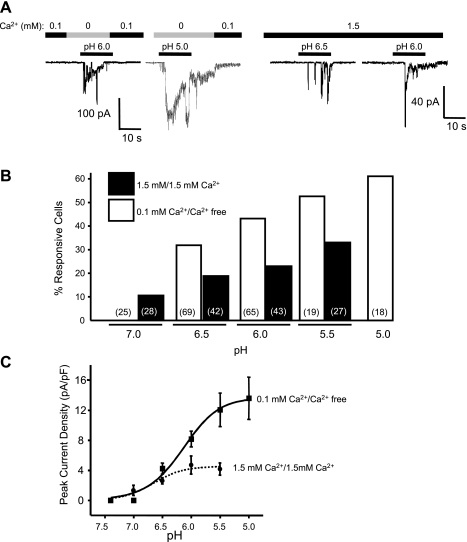
Fig. 5.
pH dependence of acid-induced inward current in freshly isolated cerebral VSMCs. A: representative traces of currents evoked by various concentrations of H+ ([H+]) when conditioned with 0.1 mM (left) and 1.5 mM Ca2+ (right). B: a tendency of pH dependence was also seen in the percentage of cells exhibiting acid-induced inward currents. C: plot of pH-current relation shows pH dependence of the peak current density (peak currents normalized to their respective membrane capacitances) in responsive cells. A pH-response curve was obtained by fitting the data to the Hill equation. The pH50 was 6.15 and 6.65 for conditioning with 0.1 and 1.5 mM Ca2+, respectively.