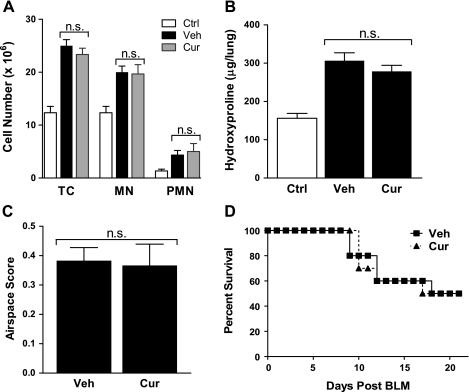
Fig. 6.
Orally administered curcumin fails to inhibit bleomycin-induced lung injury or improve survival. C57BL/6 mice were pretreated with saline (Ctrl), carboxymethylcellulose (vehicle; Veh), or curcumin (300 mg/kg) by oral gavage (o.g.). After 72 h (day 0), mice were injected with bleomycin sulphate (BLM; 0.05 units), and daily o.g. treatment was continued. A: on day 4, mice (n = 5) were killed, and lung digests were analyzed for content of total cells (TC), mononuclear cells (MN), and polymorphonuclear neutrophils (PMN). B: on day 21, mice (n = 10) were killed, and whole lung was processed for hydroxyproline content and morphometric analysis (C; n = 5). D: mortality rate of curcumin-treated and control mice (n = 10) after bleomycin (0.075 units) instillation. n.s., Not significant.